Aerfer Sagittario 2 | |
|---|---|
| Країні | Італія |
| Роль | прототип винищувача |
| Перший політ | : 19 травня 1956 |
| Побудований | 2 |
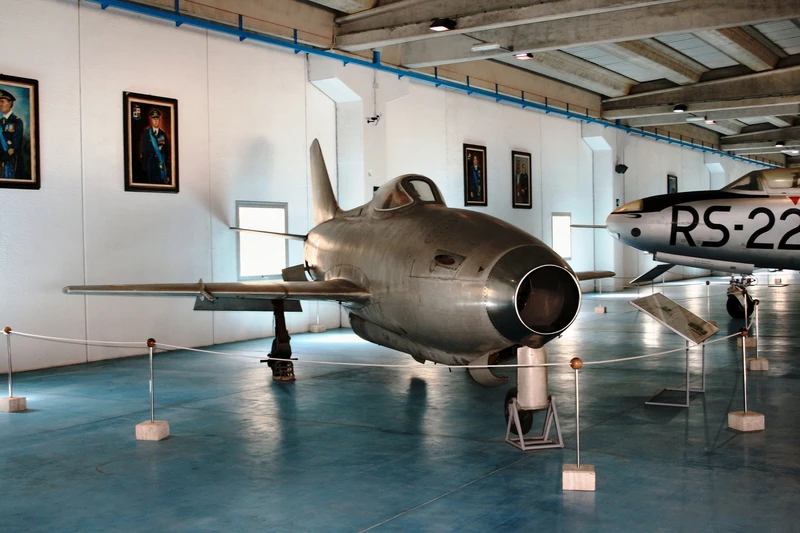
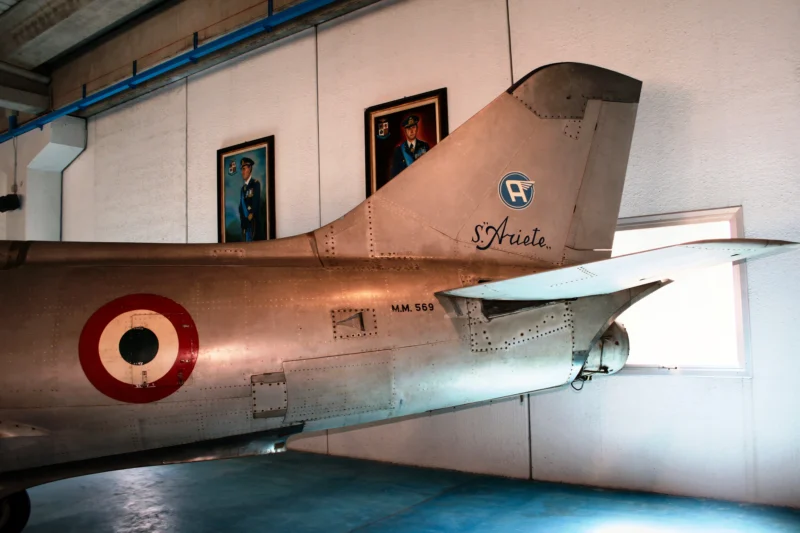
У 201 Аерфер Сагіттаріо 2 (італ. для стрільців) був прототипом суцільнометалевого одномісного легкого винищувача, побудованого в Італії компанією Aerfer, призначеного для виконання функції перехоплювача або легкого літака тактичної підтримки. Вперше піднявся в повітря в 1956 році, він став першим італійським літаком, який подолав звуковий бар'єр в керованому польоті, коли досяг 1,1 Маха під час занурення з 13 725 м (45 000 футів).
Джерело: Аерфер Сагіттаріо 2 у Вікіпедії
| Aerfer Sagittario 2 Walk Around | |
|---|---|
| Фотограф | Джакомо Грамаціо |
| Локалізацією | Незнай |
| Фото | 13 |
Читайте також:
General Characteristics
The Aerfer Sagittario 2 (Italian for “Sagittarius” or “Archer”) was an Italian prototype single-seat lightweight jet fighter developed in the mid-1950s. It is historically significant as the first Italian aircraft to break the sound barrier in a controlled flight, achieving Mach 1.1 in a dive on December 4, 1956. Developed from the piston-engined Ambrosini S.7 trainer, the Sagittario 2 was an all-metal design intended to compete for the NATO standard lightweight fighter contract, which was ultimately won by the Fiat G.91.
| Property | Typical Value (Sagittario 2) |
|---|---|
| Роль | Prototype Interceptor / Lightweight Fighter |
| Виробник | Aerfer (Aeronautica Ferrovie) |
| First Flight | May 19, 1956 |
| No. Built | 2 (Prototypes) |
| команда | 1 (Pilot) |
| Довжина | 9.50 m (31 ft 2 in) |
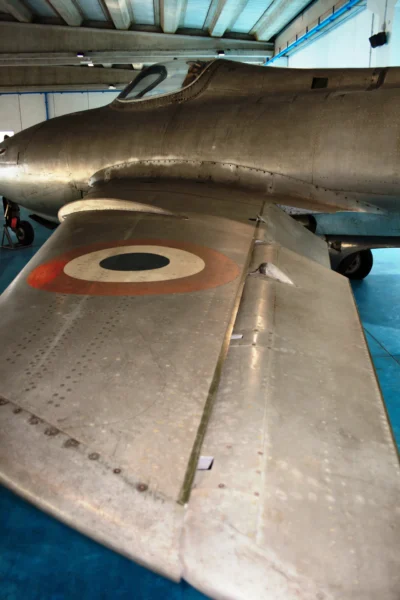
| Розмах крил | 7.50 m (24 ft 7 in) |
| Wing Area | 14.73 m² (158.6 sq ft) |
| Max Takeoff Weight | 3,293 kg (7,260 lb) |
Design and Powerplant
- Engine: One Rolls-Royce Derwent 9 centrifugal-flow turbojet.
- Thrust: 16 kN (3,600 lbf).
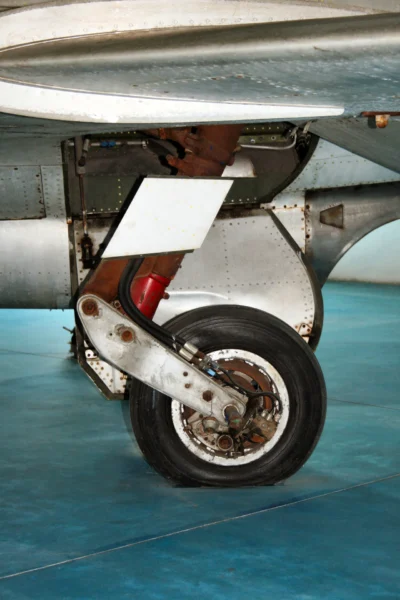
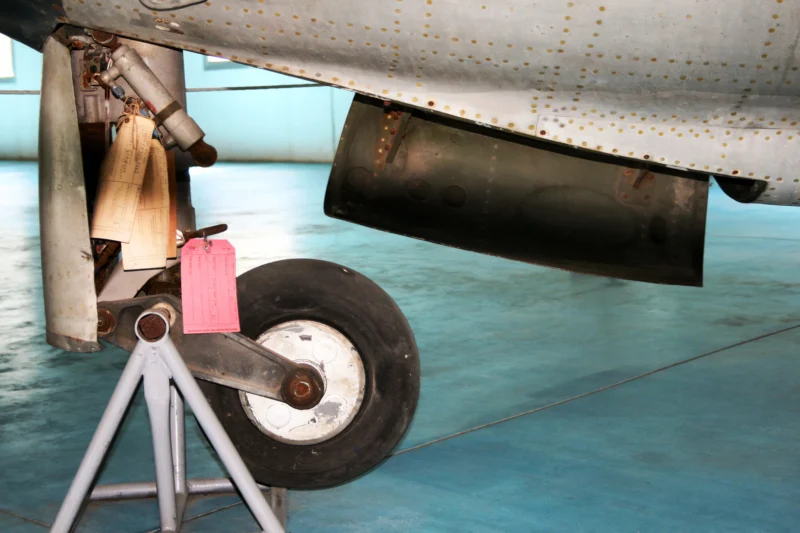
- Configuration: Low-wing, all-metal monoplane with a tricycle undercarriage. It featured highly swept wings and tail surfaces typical of early jet age designs.
- Engine Placement: The jet engine was mounted in the nose of the fuselage, with the air intake at the front and the exhaust exiting beneath the mid-fuselage. This ventral exhaust configuration was a key distinguishing feature.
- Cockpit: Equipped with a bubble canopy providing excellent visibility.
Performance and Armament
- Maximum Speed (Level Flight): Approximately 1,005–1,050 km/h (625–652 mph, 543–567 knots) at sea level.
- Mach Achievement: Reached Mach 1.1 in a controlled dive.
- Service Ceiling: 12,000 m – 14,000 m (39,000 ft – 46,000 ft).
- Rate of Climb: Approximately 42 m/s (8,300 ft/min).
- Range: 765 km (475 mi, 413 nmi).
- Fixed Armament: Two 30 mm (1.181 in) Hispano-Suiza HSS 825 L/70 cannon (nose-mounted, 300 rounds per gun capacity).
- Hardpoints: Two underwing hardpoints for external stores, with a capacity of 318 kg (701 lb), which could carry:
- Bombs: 2 x 227 kg (500 lb) bombs.
- Rockets: 12 x 7.62 cm (3 in) rockets.
- Successor: The Sagittario 2 served as the basis for the more advanced, but still experimental, Aerfer Ariete, which added a Rolls-Royce Soar auxiliary jet engine for enhanced climb performance.
Кількість переглядів : 769