Lun klasės ekranoplanas | |
|---|---|
| Šalies | Sovietų Sąjunga |
| Vaidmenį | Atakos / transporto priemonės poveikio transporto priemonė |
| Tarnyboje | 1987–1990 m. pabaiga |
| Pastatytas | 2 |
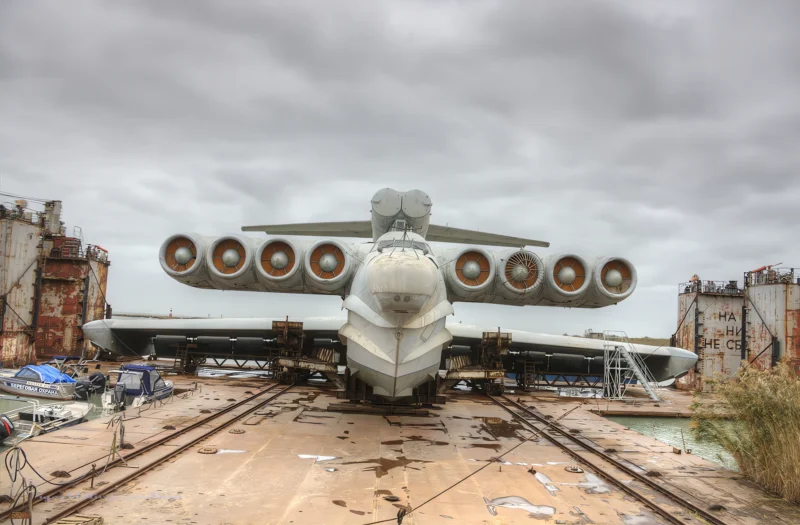
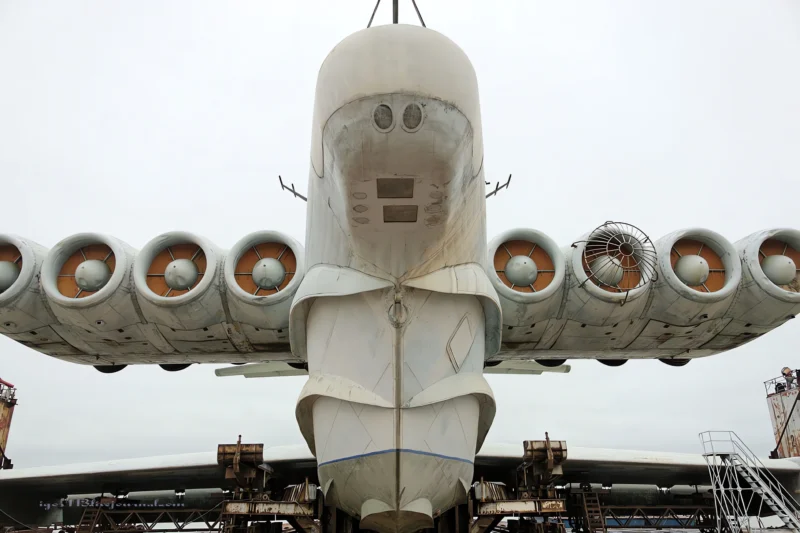
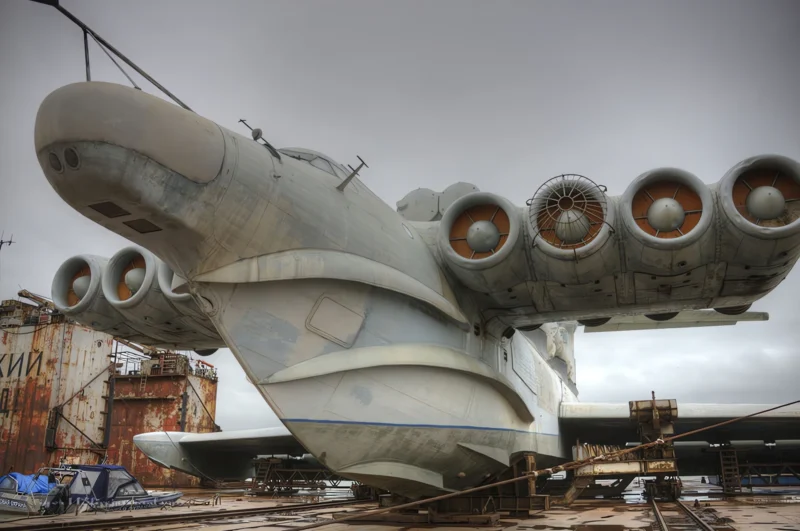
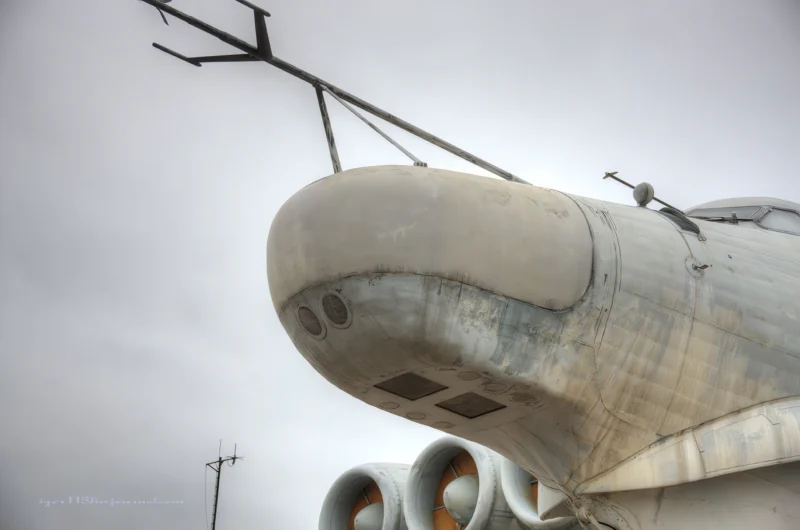
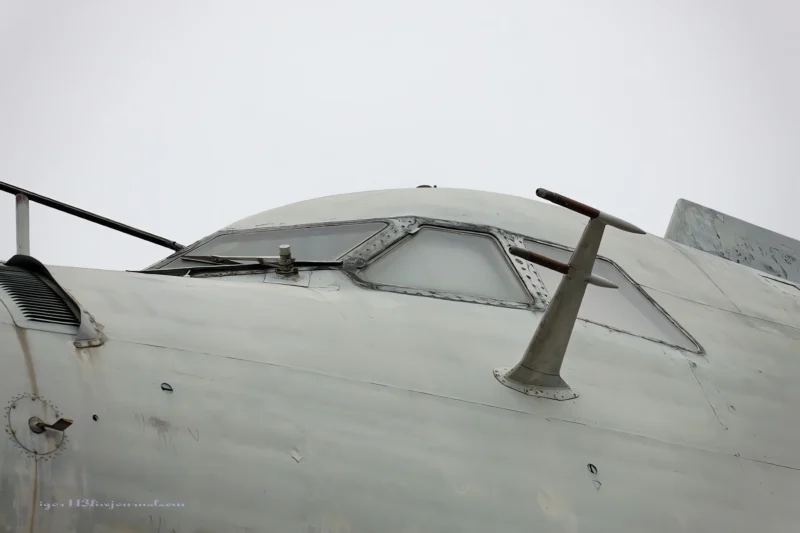
2007 Lun klasės ekranoplanas (also called Project 903) is a ground effect vehicle (GEV) designed by Rostislav Alexeyev in 1975 and used by the Soviet and Russian navies from 1987 until sometime in the late 1990s. It flew using lift generated by the ground effect acting on its large wings when within about four metres (13 ft) above the surface of the water. Although they might look similar to traditional aircraft, ekranoplans like the Lun are not classified as aircraft, seaplanes, hovercraft, or hydrofoils. Rather, crafts like the Lun-class ekranoplan are classified as maritime ships by the International Maritime Organization due to their use of the ground effect, in which the craft glides just above the surface of the water.
Šaltinis: Lun klasės ekranoplan Vikipedijoje
| "Lun" Ekranoplan Vaikščioti aplink | |
|---|---|
| Fotografas | Igoris Kolokolovas |
| Lokalizavimo | Nežinoti |
| Nuotraukos | 158 |
| Ekranoplanas Lunas vaikšto aplinkui | |
|---|---|
| Fotografas | Nežinoti |
| Lokalizavimo | |
| Nuotraukos | 88 |
Taip pat žiūrėkite:
General Characteristics
The Lun-class Ekranoplan was a massive, high-speed military vehicle developed in the Soviet Union. Classified officially as a ship, it operated by using the ground effect, flying mere meters above the water surface at high speed to avoid naval mines and circumvent obstacles.
| Property | Value (MD-160 Variant) |
|---|---|
| Vaidmenį | Missile Launcher / Fast Attack GEV |
| Dizaineris | Rostislav Evgenievich Alexeyev (Central Hydrofoil Design Bureau) |
| First Flight | 1985 (Approximate) |
| Įgulos | 10 (Officers and Crew) |
| Konfigūracija | Low-wing monoplane, Ground Effect Vehicle (GEV) |
| Maximum Displacement | Approx. 380 tonnes |
| Skaičius pastatytas | 1 (Only one missile-equipped Lun was completed) |
Powerplant and Design
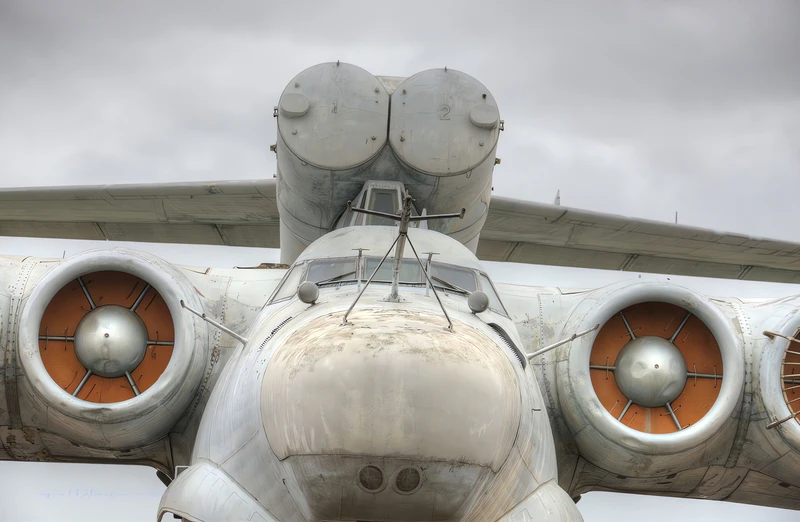
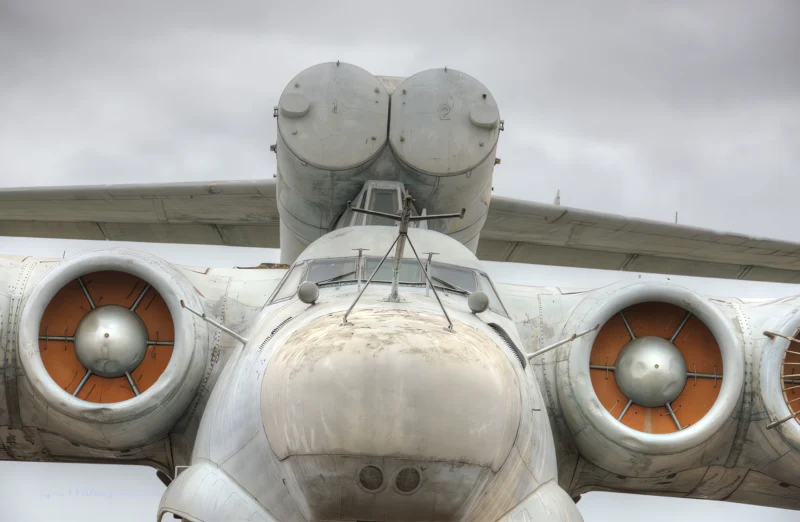
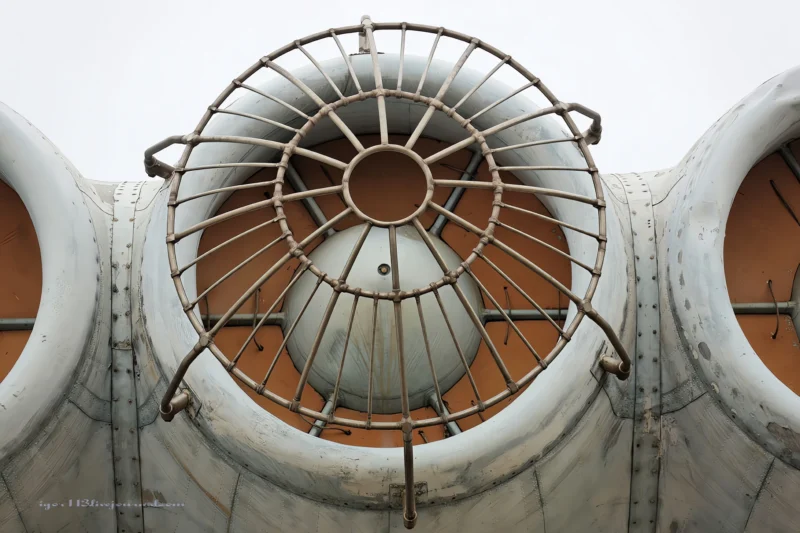
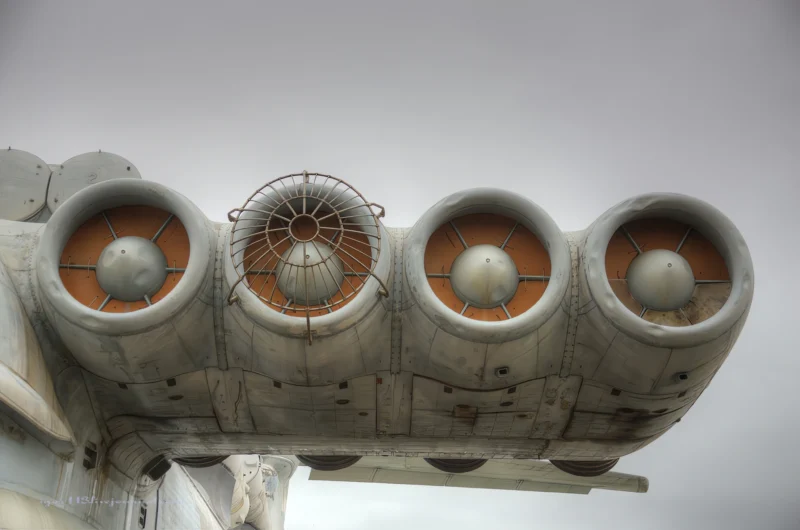
- Powerplant: Eight Kuznetsov NK-87 turbofan engines.
- Engine Placement: Mounted in pairs on eight individual nacelles located on the front of the forward main wing/canard structure.
- Thrust: Approx. 127.4 kN (28,600 lbf) per engine.
- Ground Effect Principle: The engines were placed high to allow the jet exhaust to create a cushion of high-pressure air beneath the wings, lifting the massive craft (known as the coanda effect).
- Hull: Designed with a deep V-shape hull, allowing it to land and take off on water, and withstand relatively high waves (up to 2.5 meters).
Armament and Performance
- Armament: Six P-270 Moskit (SS-N-22 Sunburn) anti-ship missile launchers (three located on either side of the hull, just behind the cockpit).
- Maximum Speed: Up to 550 km/h (340 mph / 300 knots).
- Operational Altitude: Typically 1.5 to 5 meters above the water surface.
- Operational Range: Approximately 2,000 km (1,200 miles).
- Status: The sole missile-armed Lun was decommissioned in the late 1990s and currently resides as a museum piece in Derbent, Dagestan.
Views : 1931