Custer CCW-5 | |
|---|---|
| Land | Usa |
| Rolle | 5-Sitzer Leichter Transport |
| Erstflug | 13. Juli 1953 |
| Gebaut | 2 |
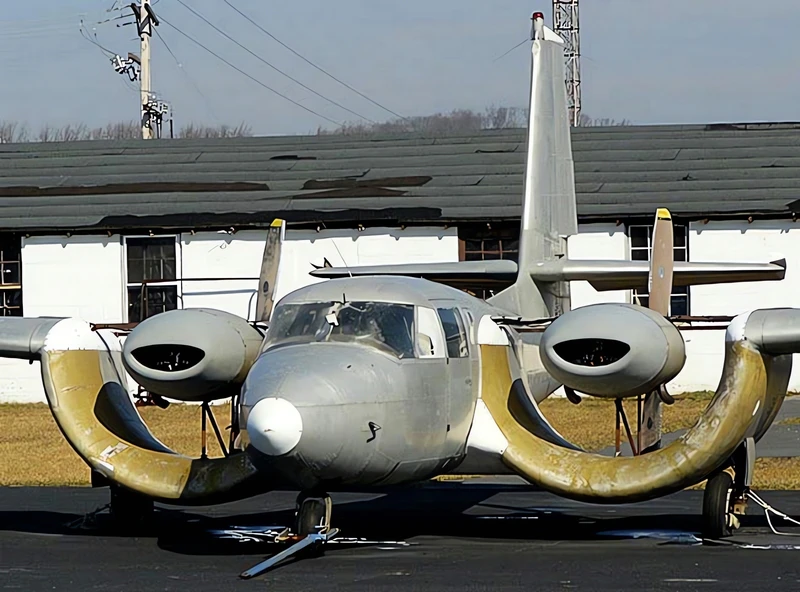
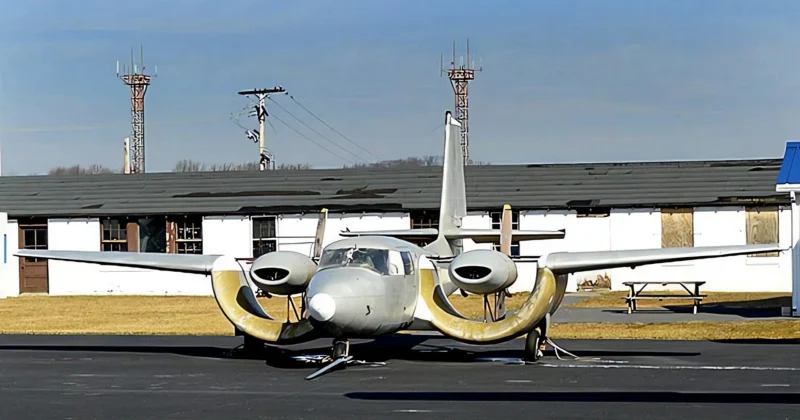
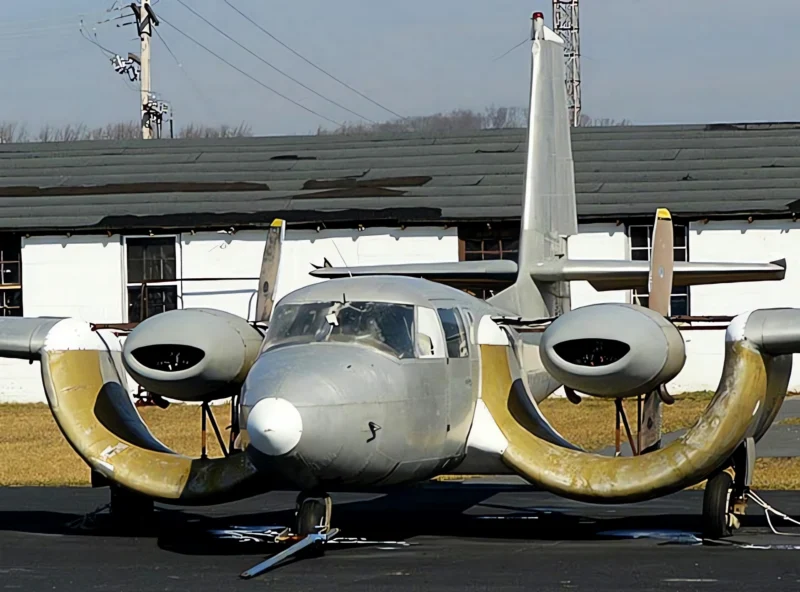
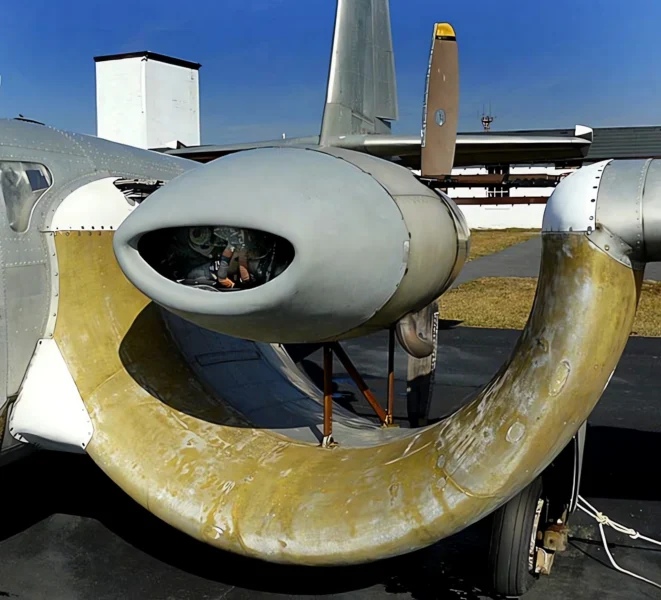
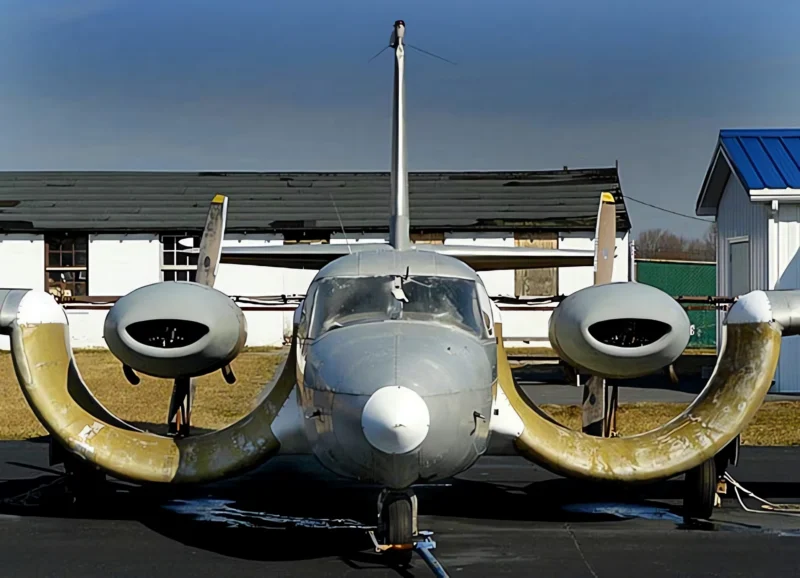
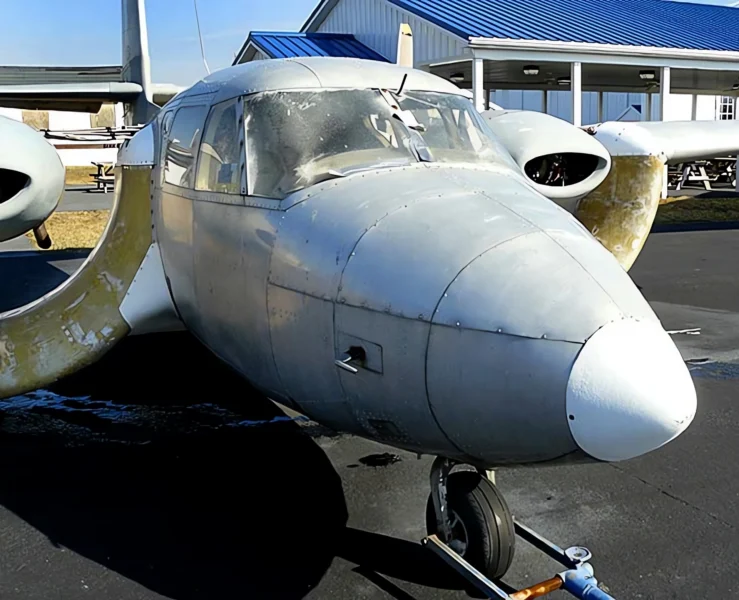
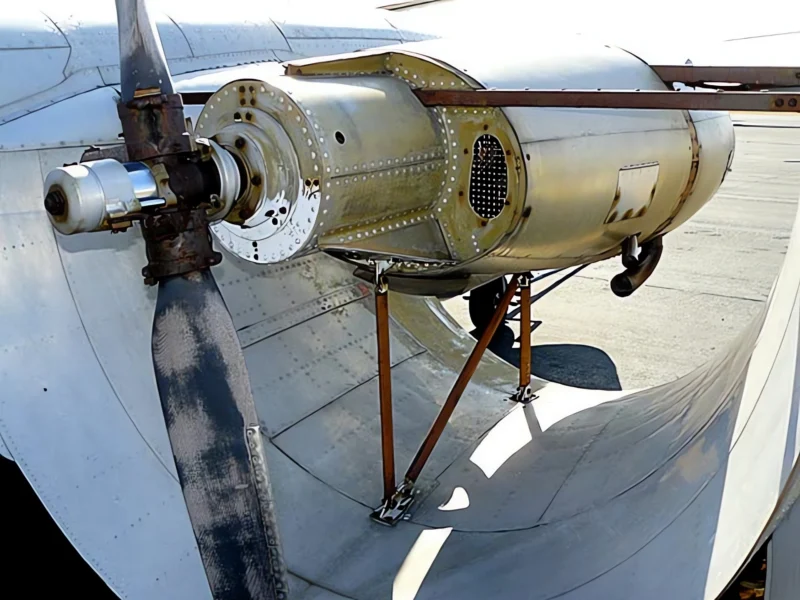
das Custer CCW-5 was a twin-engined, 5-seat aircraft of pusher configuration, which used a channel wing claimed to enable low speed flight and short take-offs. Two CCW-5s flew, eleven years apart, but the type never entered production. The aircraft was the third and last of a series of Custer Channel Wing designs.
Quelle: Custer CCW-5 auf Wikipedia
| Custer Channel Wing CCW-5 STOL Walk Around | |
|---|---|
| Photographer | Bill Maloney |
| Localisation | Unknow |
| Photos | 19 |
Siehe auch:
General Characteristics and Role
The Custer Channel Wing CCW-5 was an experimental American short takeoff and landing (STOL) aircraft designed to demonstrate the unique Channel Wing concept developed by Willard Custer. This unique design features a pair of semi-circular or U-shaped channels mounted on the leading edge of the wing, with the engine propellers positioned at the rear of these channels. The propellers draw air over the channels, creating a massive increase in lift even at low airspeeds, allowing the aircraft to achieve exceptionally short takeoff and landing distances. The CCW-5 was the largest and final variant built, intended for potential commercial or military use as a utility transport. The design showed significant promise in achieving STOL performance but ultimately did not enter mass production due to complexity and certification challenges.
| Property | Typical Value (CCW-5) |
|---|---|
| Rolle | Experimental STOL Aircraft, Utility Transport Prototype |
| National Origin | USA |
| Hersteller | Custer Channel Wing Corporation |
| First Flight | 1964 (CCW-5) |
| Crew | 2 (Pilot, Co-pilot) |
| Fassungsvermögen | 3 passengers (or cargo) |
| Länge | 8.43 m (27 ft 8 in) |
| Wingspan (Conventional) | 12.42 m (40 ft 9 in) |
| Höhe | 2.69 m (8 ft 10 in) |
| Empty Weight (Approx.) | 1,814 kg (4,000 lb) |
| Max Takeoff Weight (Approx.) | 2,722 kg (6,000 lb) |
Powerplant and Performance
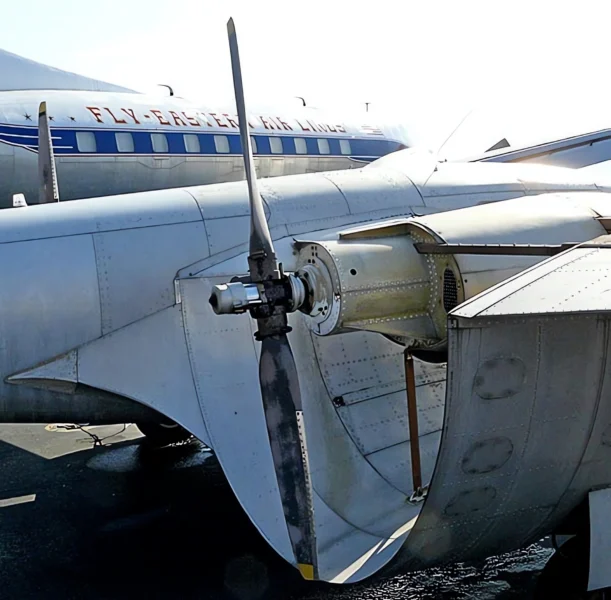
- Engine: 2 x Lycoming O-540-A series six-cylinder, air-cooled piston engines.
- Power Output (Per Engine): 194 kW (260 hp).
- Maximum Speed: 320 km/h (200 mph; 170 kn).
- Cruise Speed: 290 km/h (180 mph; 160 kn).
- Takeoff Distance (STOL Claim): Less than 60 meters (200 ft).
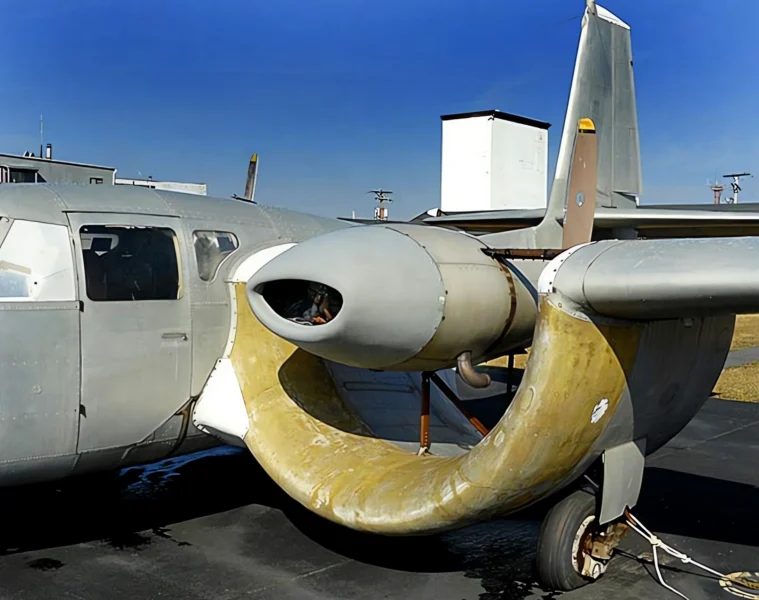
- Channel Wing Concept: The channels essentially use propeller thrust to create a low-pressure area over the top of the wing segment, increasing the effective camber and generating lift far in excess of conventional wings at the same airspeed.
Design Origin and Legacy
- Origin: The CCW-5 was a conversion of a standard Grumman Cougar twin-engine aircraft, replacing the conventional wing and engine nacelles with the Channel Wing system.
- Custer’s Patent: The Channel Wing principle was patented by Willard Custer in 1951, theorizing that the forced airflow through the semi-circular channels would create “super-circulation” and exceptional lift.
- Military Interest: The US military showed brief interest in the CCW design for its potential use in forward-area resupply due to the STOL capability, but no major contracts materialized.
- Status: The CCW-5 and its predecessors remain significant examples of unconventional aerodynamic experiments aimed at achieving practical vertical/short takeoff and landing (V/STOL) flight.
Aufrufe : 1658