USS Requin SS-481 | |
|---|---|
| Country | USA |
| Class and type | Tench-class diesel-electric submarine |
| Launched | 1 January 1945 |
| Decommissioned | 2 December 1968 |
USS Requin (SS/SSR/AGSS/IXSS-481), a Tench-class submarine, was the only ship of the United States Navy to be named after the requin, French for shark. Since 1990 it has been a museum ship at The Carnegie Science Center in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Her keel was laid down on 24 August 1944 by the Portsmouth Navy Yard in Kittery, Maine. She was launched on 1 January 1945 sponsored by Mrs. Slade D. Cutter, and commissioned on 28 April 1945 with Commander Slade D. Cutter in command.
Source: USS Requin on Wikipedia
| USS Requin Walk Around | |
|---|---|
| Photographer | Bill Maloney |
| Localisation | Unknow |
| Photos | 225 |
See also:
General Characteristics and Role
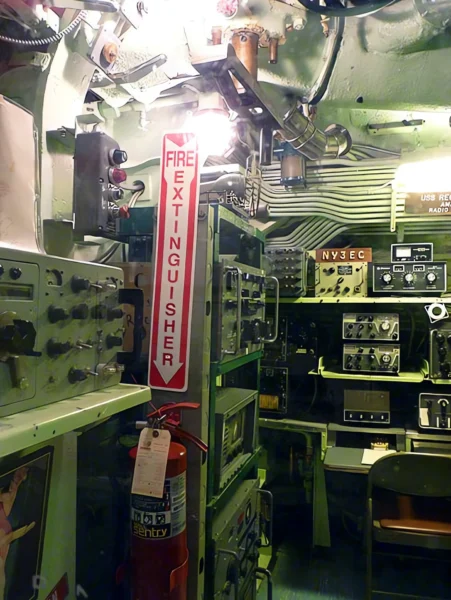
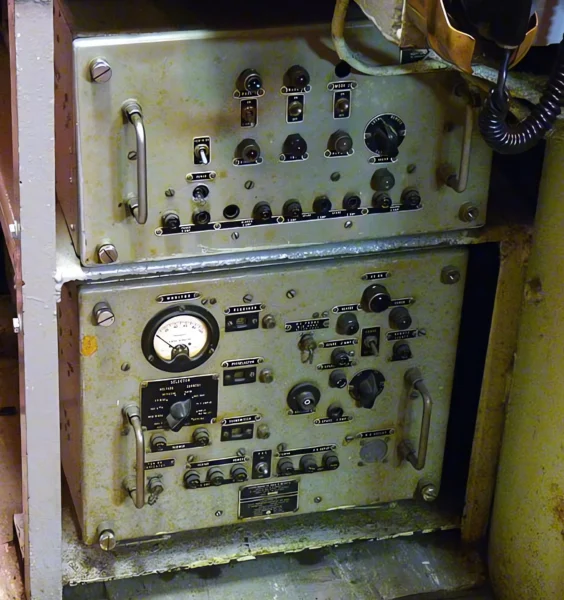
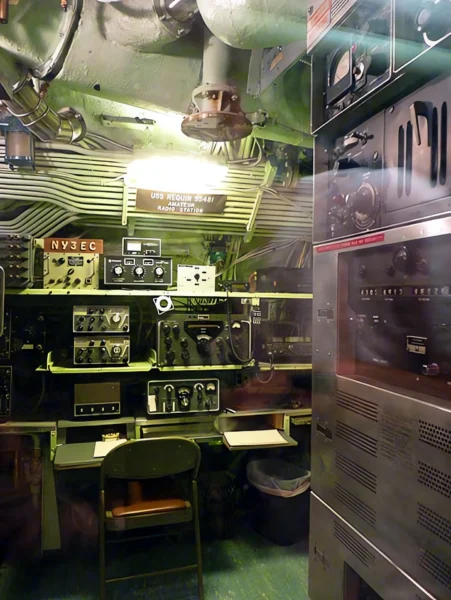
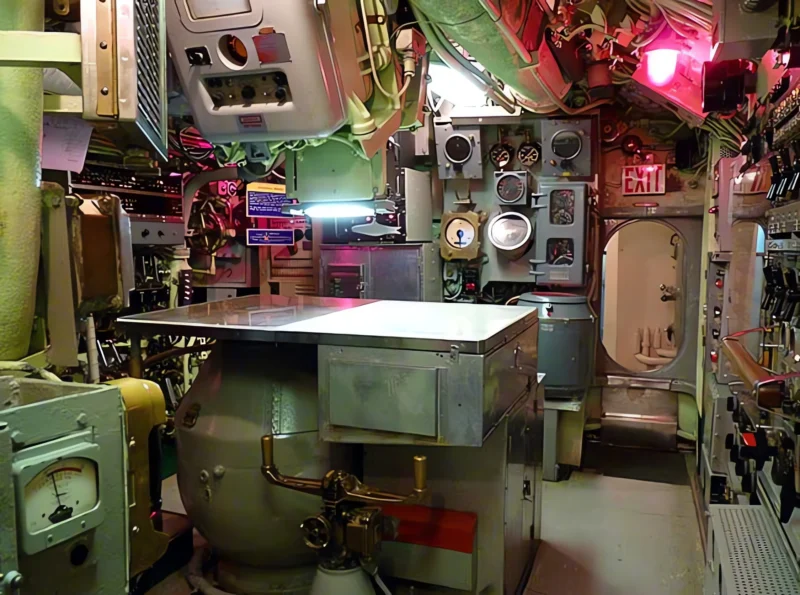
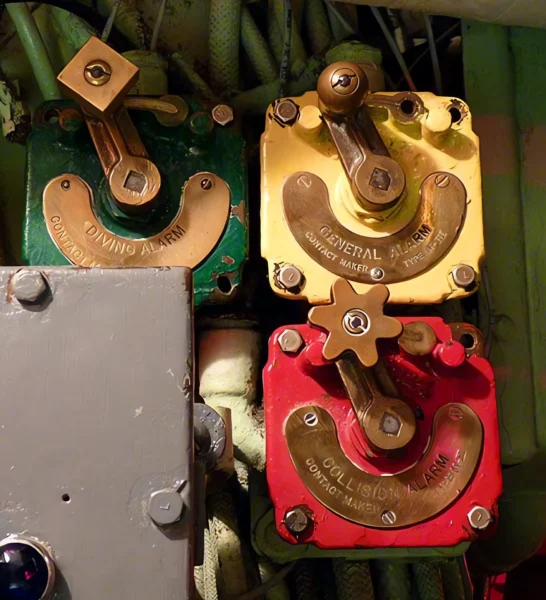
The USS Requin (pronounced “RAY-kwin”), French for “shark,” is a Tench-class diesel-electric submarine of the United States Navy. Commissioned late in World War II, the Requin arrived in the Pacific after hostilities ended and therefore did not see combat. It is famous for its unique service life, being the first U.S. Navy submarine converted to a radar picket (SSR-481) under Project Migraine in 1946. In this role, it was equipped with advanced radar to detect aircraft at long range, operating as an early warning station during the Cold War. It underwent another conversion in 1959 to a Fleet Snorkel submarine (SS-481). The Requin is now preserved as a museum ship at the Carnegie Science Center in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.
| Property | Typical Value (As Built – Tench Class) |
|---|---|
| Class & Type | Tench-class Diesel-Electric Submarine |
| National Origin | United States |
| Builder | Portsmouth Naval Shipyard, Kittery, Maine |
| Commissioned | 28 April 1945 |
| Displacement (Surfaced) | 1,570 long tons (1,595 t) |
| Displacement (Submerged) | 2,414 long tons (2,453 t) |
| Length Overall | 95.02 m (311 ft 9 in) |
| Beam | 8.33 m (27 ft 4 in) |
| Test Depth | 126 m (412 ft) |
| Complement | 10 officers, 71 enlisted men |
Powerplant and Performance
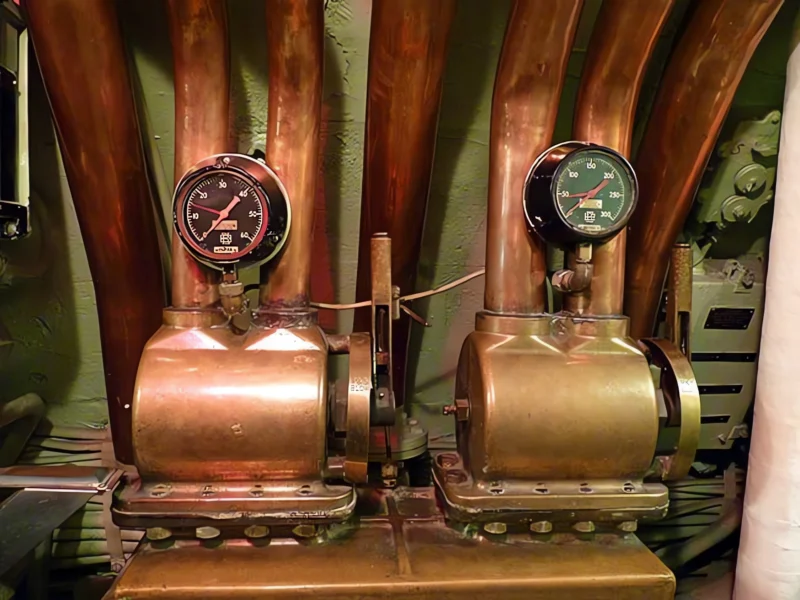
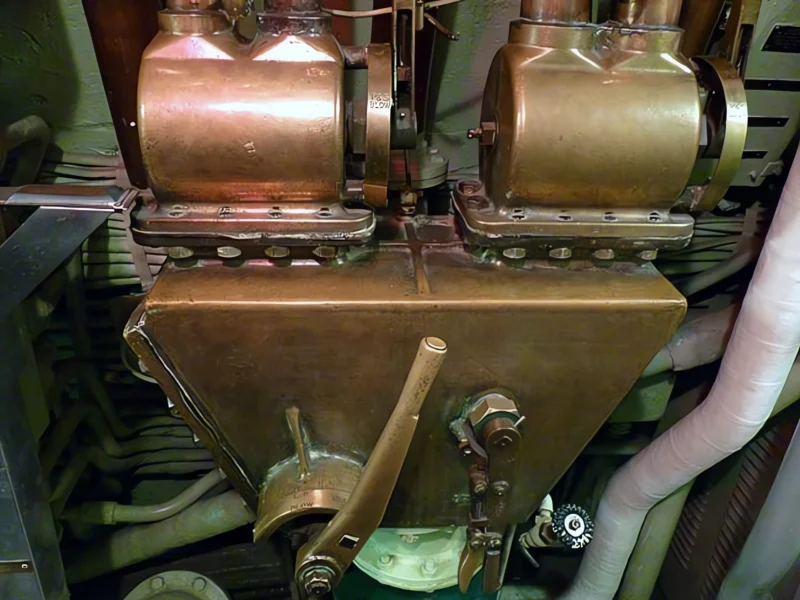
- Powerplant (Main): 4 x Fairbanks-Morse Model 38D8-⅛ opposed-piston diesel engines driving electrical generators.
- Propulsion: 2 x Elliott electric motors driving two propeller shafts.
- Shaft Horsepower: 5,400 shp (Surfaced); 2,740 shp (Submerged).
- Maximum Speed: 20.25 knots (38 km/h) surfaced; 8.75 knots (16 km/h) submerged.
- Range: 11,000 nautical miles at 10 knots surfaced.
- Endurance: 75 days on patrol; 48 hours submerged at 2 knots.
Armament and Conversions
- Armament (As Built): 10 x 21-inch (533 mm) torpedo tubes (6 bow, 4 stern), carrying 28 torpedoes. Initially carried a heavier-than-standard armament including a 5-inch deck gun, 40 mm, and 20 mm anti-aircraft guns.
- Radar Picket Conversion (SSR-481): Aft torpedo tubes, deck guns, and aft anti-aircraft guns were removed. A large mast housing surface and air-search radar was installed, along with a Combat Information Center (CIC) in the stern room.
- Fleet Snorkel Conversion (SS-481): The radar picket equipment was removed, and a modernized snorkel breathing apparatus was installed, allowing diesel engine operation at periscope depth.
- Museum Status: Decommissioned in 1968. Has been a museum ship in Pittsburgh, PA since 1990.
Views : 1080