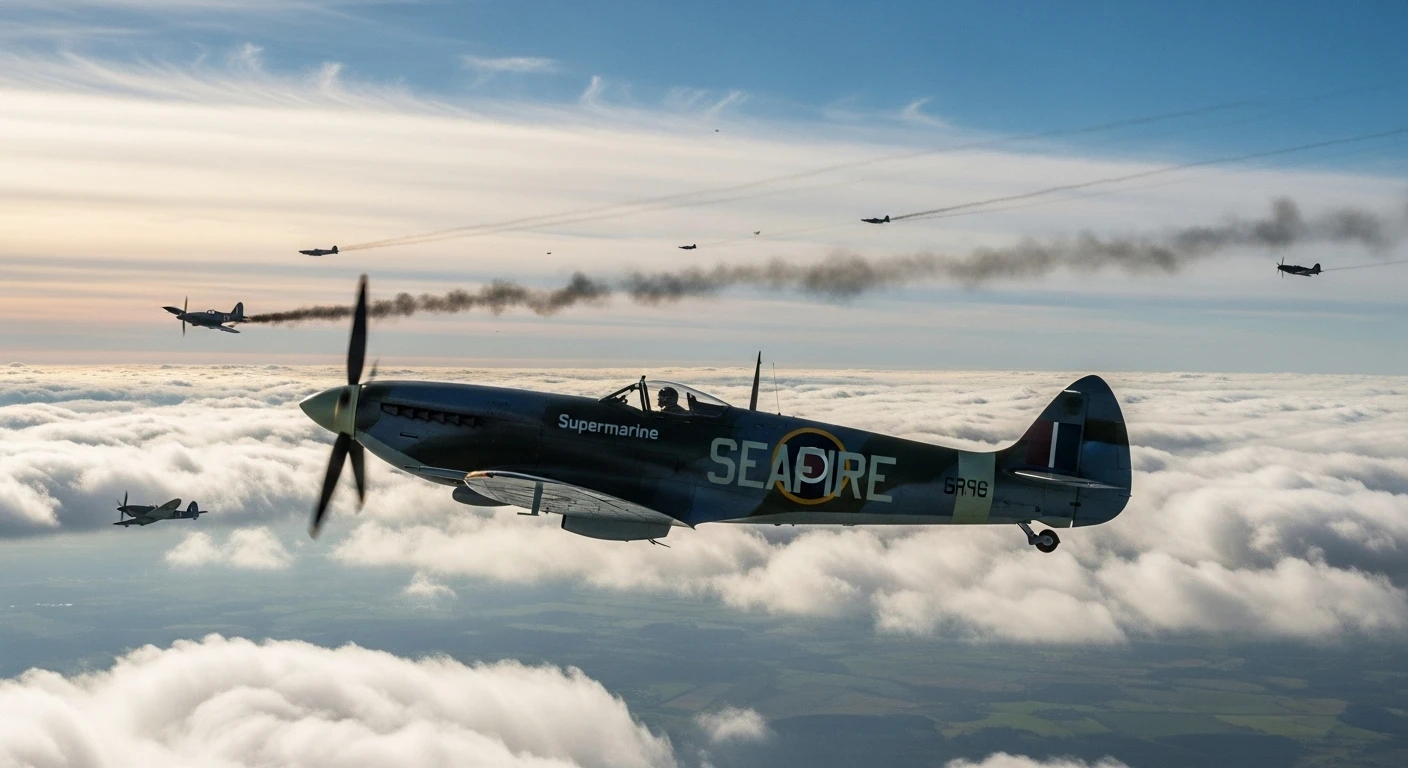
Supermarine Seafire | |
|---|---|
| Country | UK |
| Role | Carrier-based fighter |
| First flight | 7 January 1942 |
| Built | 2646 |
el Supermarine Seafire es una versión naval del Supermarine Spitfire adaptada para operar desde portaaviones.
Fuente: Wikipedia
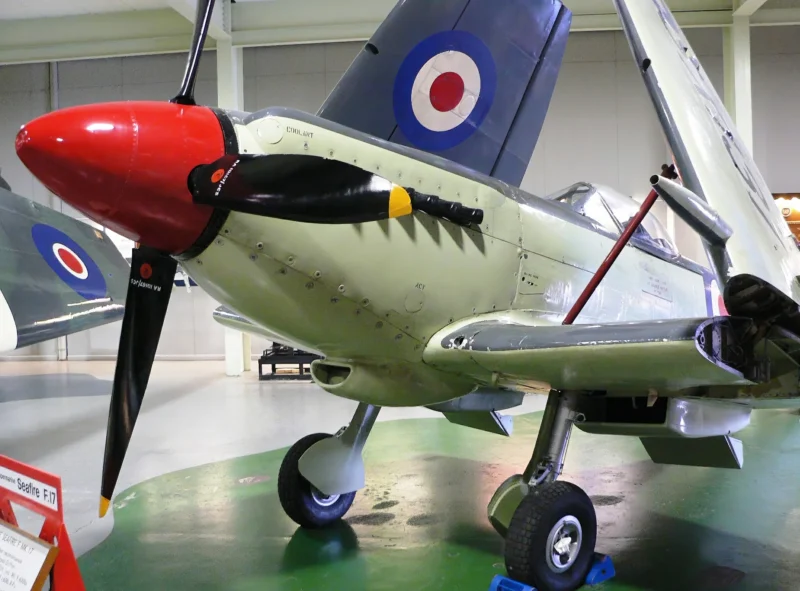
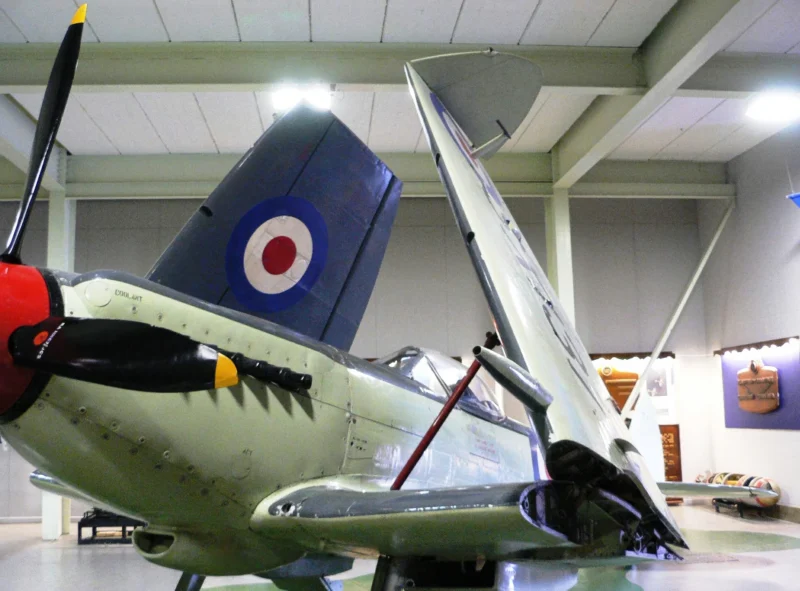
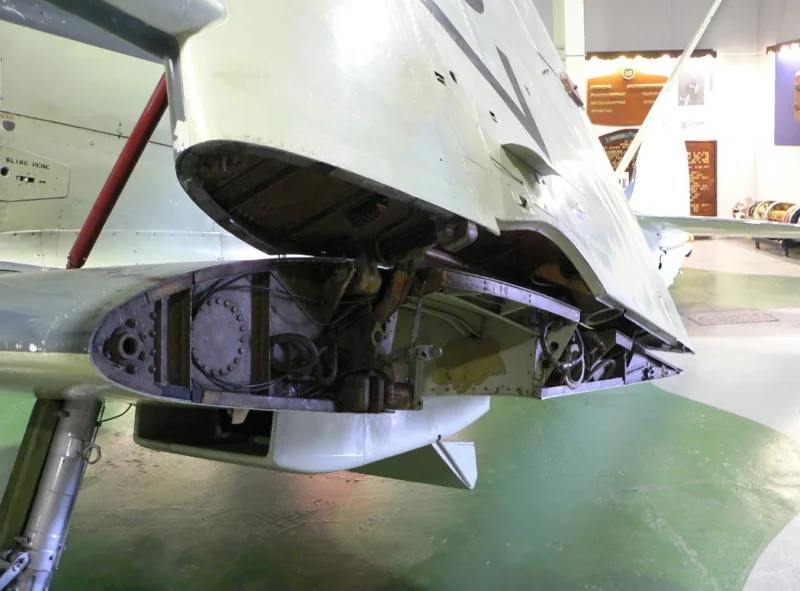
| Supermarine Seafire F Mk.17 Walk Around | |
|---|---|
| Fotógrafo | Unknow |
| Localización | Unknow |
| Fotos | 47 |
Ver también:
The Spitfire Goes to Sea
el Supermarine Seafire was the carrier-based adaptation of the legendary Spitfire. While the Royal Navy initially relied on slower aircraft like the Fulmar, the desperate need for a high-performance interceptor to combat the Luftwaffe and Japanese Zeros led to the “navalization” of the Spitfire airframe. It was a trade-off: the Seafire brought world-class speed and agility to the Fleet Air Arm, but its land-based DNA made it notoriously difficult to land on a moving, pitching carrier deck.
| Attribute | Standard Specification (Seafire Mk III / Mk 47) |
|---|---|
| Papel | Carrier-based Fighter / Interceptor |
| Primary Engine | Rolls-Royce Merlin 55M (Mk III) / Griffon 88 (Mk 47) |
| Horsepower | 1,585 hp (Mk III) / 2,350 hp (Mk 47) |
| Armamento principal | 2 × 20mm Hispano cannons & 4 × .303 Browning MGs |
| Velocidad máxima | 578 km/h (359 mph) for Mk III / 727 km/h (452 mph) for Mk 47 |
| Stall/Landing Speed | Approx. 150 km/h (95 mph) — High for carriers |
| Empty Weight | 2,412 kg (5,317 lbs) |
| Total Production | 2,646 (All variants) |
Design Challenges & Modifications
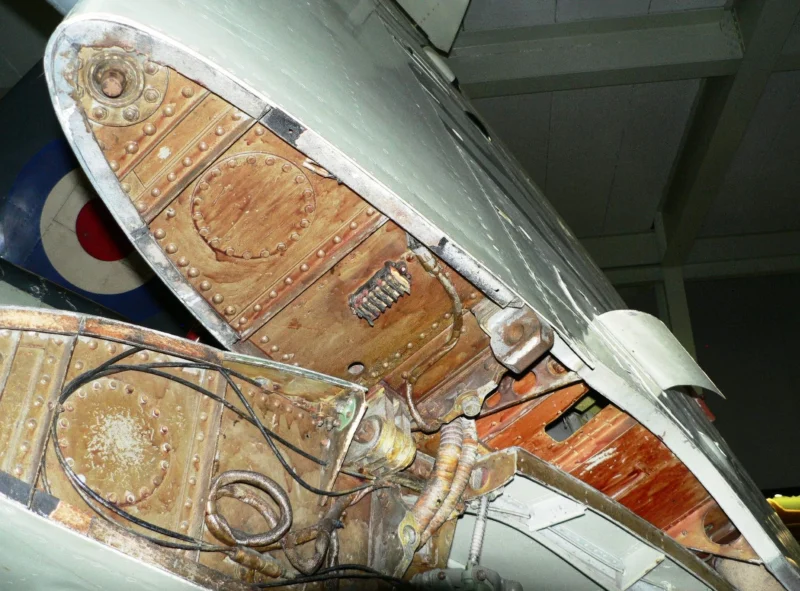
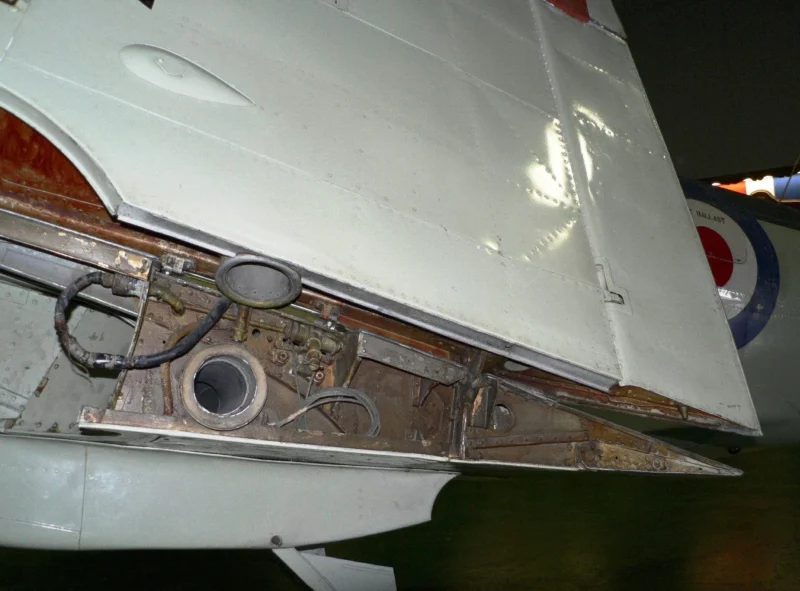
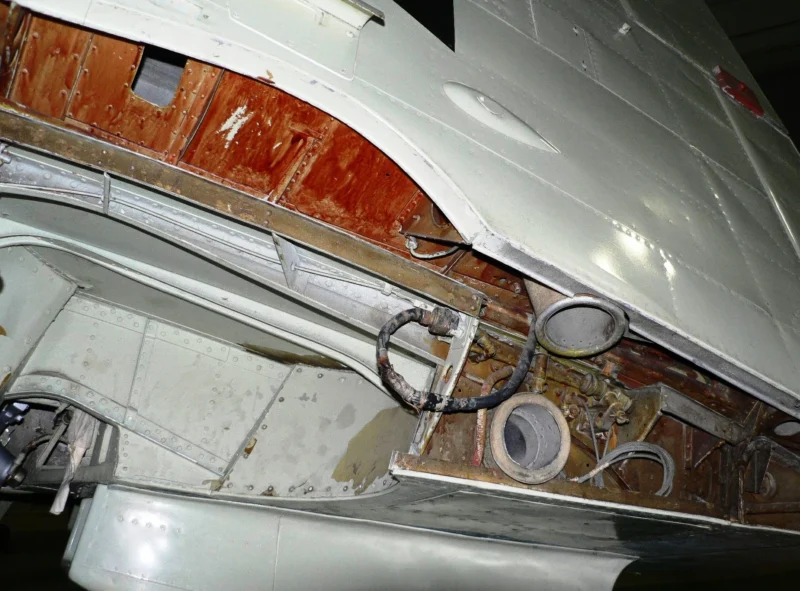
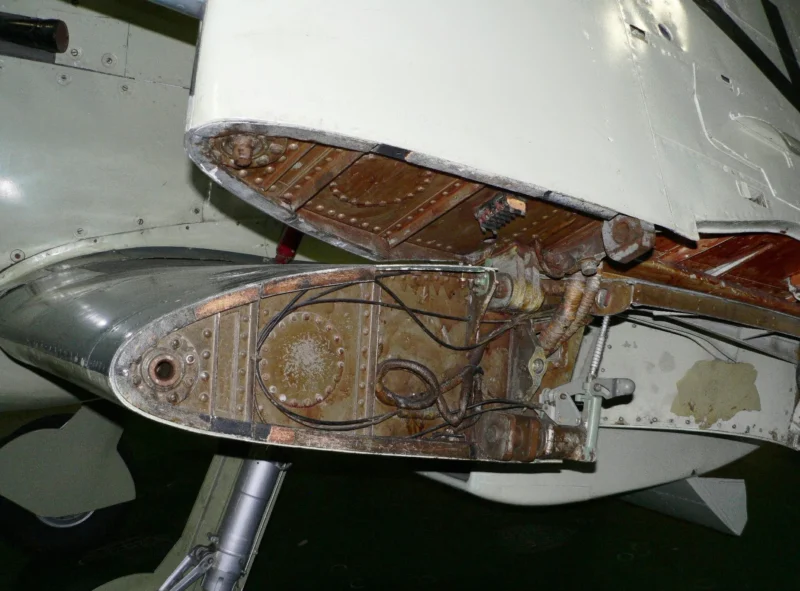
- The “Sting” Hook: Early Seafires were simply “hooked Spitfires.” Later models featured a reinforced “A-frame” or “Sting” type arrestor hook to handle the massive deceleration of a carrier trap.
- Folding Wings: Because the Spitfire’s elliptical wing was never meant to fold, the Seafire Mk III introduced a manual folding mechanism where the wingtips folded down and the main panels folded up, allowing it to fit into tight carrier hangars.
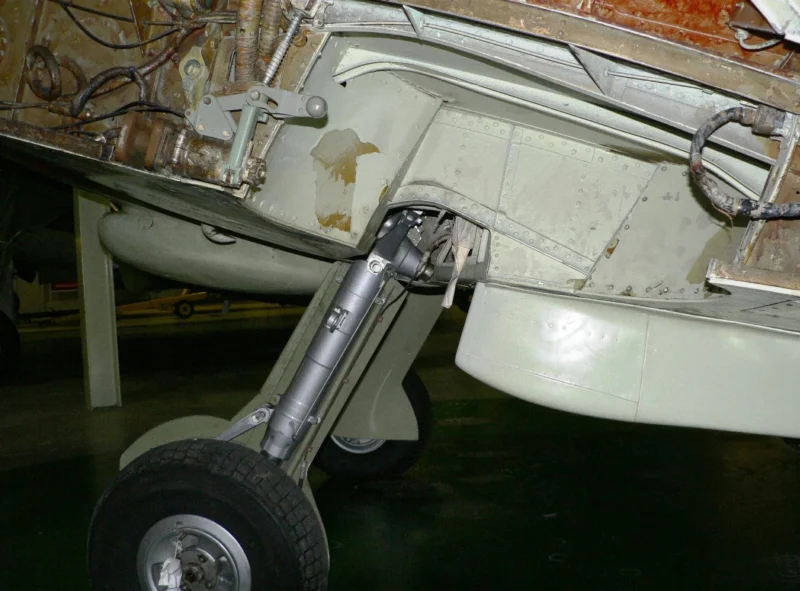
- Narrow Landing Gear: The Seafire’s biggest weakness was the Spitfire’s narrow-track undercarriage. On a rolling deck, this led to frequent “ground loops” and collapses, causing more losses to accidents than to enemy combat.
- The Griffon Evolution: The ultimate version, the Seafire Mk 47, featured the massive Griffon engine and contra-rotating propellers to cancel out the immense torque that otherwise made carrier takeoffs dangerous.
Operational Legacy
- Operation Torch: The Seafire made its combat debut in 1942 during the invasion of North Africa, providing vital air cover for the fleet.
- Kamikaze Hunter: In the Pacific, the Seafire’s incredible rate of climb made it the preferred interceptor for “Jack” patrols—standing by to intercept Japanese Kamikazes at a moment’s notice.
- The Korean War: The Seafire 47 served with distinction in the opening stages of the Korean War (1950) before being replaced by the more rugged Hawker Sea Fury.
Vistas: 2122