Mirage Dassault 2000D | |
|---|---|
| Pays | France |
| Rôle | Bombardier tactique |
| Premier vol | Le 3 février 1986 |
| Construit | 86 |
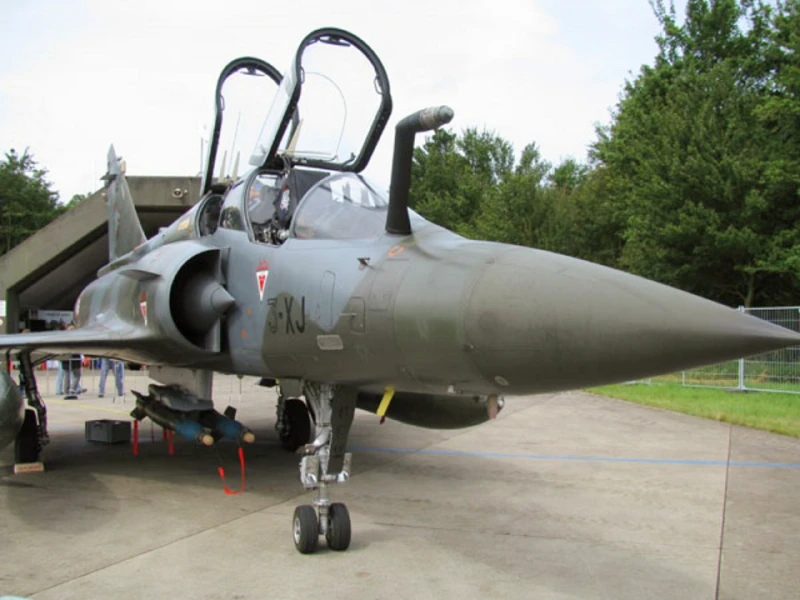
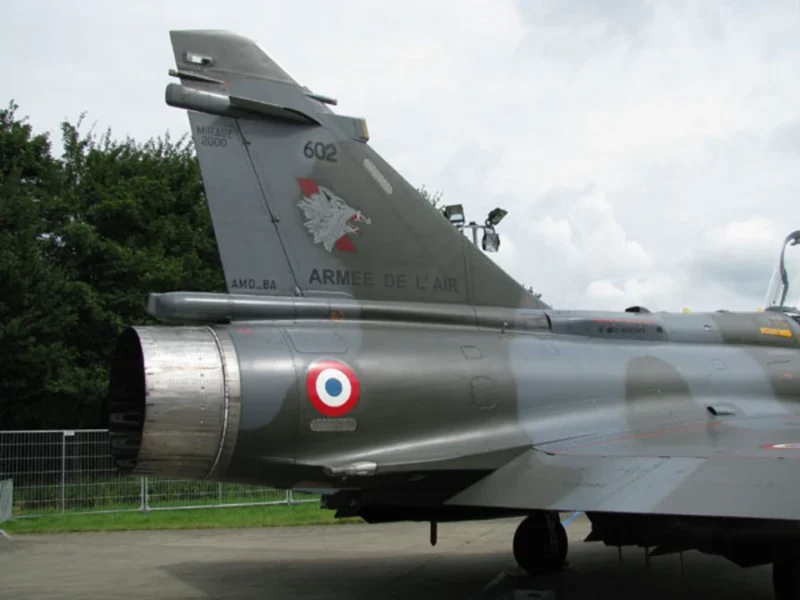
Le Mirage 2000N de Dassault est une variante du Mirage 2000 conçu pour la frappe nucléaire. Il constitue le cœur de la Français de dissuasion nucléaire tactique basée sur l’air. Lla Mirage 2000D is its conventional attack counterpart. Dassault has also developed the Mirage 2000D, which is a development of the Mirage 2000N designed for long-range precision strikes with conventional weapons. This aircraft is exactly the same as the Mirage 2000N, but introduces support for conventional attack missiles such as the Apache and Scalp missiles, as well as the AASM weapons. The first aircraft, converted from the Mirage 2000N prototype, flew on 19 February 1991, and the French Air Force ordered a total of 86 aircraft.
| Mirage 2000 prototype Walk Around | |
|---|---|
| Photographe | Meindert de Vreeze |
| Localisation | Inconnu |
| Photos | 43 |
Voir aussi :
The Return of the Delta
Lla Mirage Dassault 2000 was a bold return to the classic tailless delta-wing formula that made the original Mirage III famous. Developed in the late 1970s to replace the Mirage F1, it was designed to be a lightweight, high-altitude interceptor capable of Mach 2.2. By combining the sleek delta shape with modern Fly-By-Wire technology, Dassault created an aircraft that fixed the old delta-wing weaknesses (high landing speeds and poor maneuverability) while retaining its incredible speed and climb rate.
| Attribute | Technical Specification (Mirage 2000-5) |
|---|---|
| Rôle | Multi-role Fighter / Interceptor |
| Crew | 1 (Single seat) or 2 (B/D/N variants) |
| First Flight | March 10, 1978 |
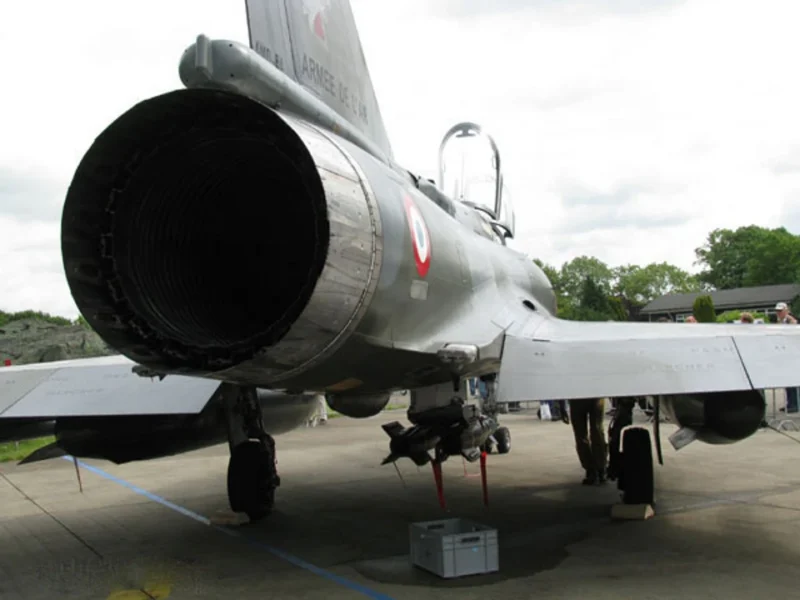
| Groupe motopropulseur | 1 × SNECMA M53-P2 afterburning turbofan |
| Thrust | 21,400 lbf (95 kN) with afterburner |
| Vitesse maximale | Mach 2.2 (2,330 km/h) |
| Service Ceiling | 59,000 feet (18,000 m) |
| Armement | 2 × 30mm DEFA cannons; 9 hardpoints (up to 6,300 kg) |
Aerodynamic Prowess & Fly-By-Wire
- Relaxed Static Instability: The Mirage 2000 is designed to be naturally unstable. This means it wants to « tumble, » but a computer-controlled Fly-By-Wire system makes thousands of tiny adjustments per second to keep it flying. This makes it incredibly « twitchy » and responsive in a dogfight.
- Low-Drag Delta: Because it lacks a horizontal tail (stabilators), the Mirage 2000 has very low drag at high speeds. It can accelerate from Mach 0.9 to Mach 1.4 in just seconds, making it a premier interceptor for the « Quick Reaction Alert » (QRA) role.
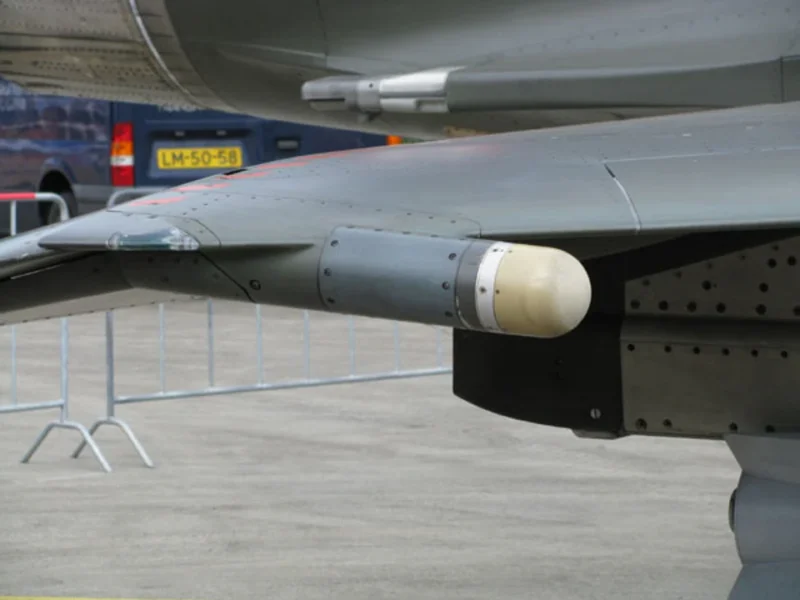
- Lla « Shock Cone » Intakes: The air intakes feature movable half-cones (called « souris » or mice) that slide forward and backward automatically to manage the airflow into the engine at supersonic speeds.
- Integrated Avionics: The 2000-5 variant introduced the RDY radar, which was one of the first European radars capable of tracking multiple targets and firing « fire-and-forget » MICA missiles simultaneously.
Combat Variants & Global Impact
- Mirage 2000N (Nucleaire): Lla « N » variant was designed for low-level, high-speed nuclear strike missions, carrying the ASMP missile. It featured a strengthened airframe to withstand the turbulence of flying at 600 knots just feet above the ground.
- Mirage 2000D (Diversifié): A two-seat conventional ground-attack version. It lacks internal cannons but can carry a massive array of precision-guided munitions (PGMs) and laser-targeting pods.
- The Kargil Hero: During the 1999 Kargil War, the Indian Air Force used Mirage 2000s to drop laser-guided bombs at extreme altitudes, proving the aircraft’s effectiveness in mountain warfare where other jets struggled.
- Export Success: The Mirage 2000 has been a major success on the international market, serving with distinction in Greece, Taiwan, the UAE, Qatar, Egypt, Peru, and Brazil.
Views : 7478