HMS Cavalier (R73) | |
|---|---|
| Pays | Royaume-Uni |
| Classe et type | Destroyer de classe C |
| Lancé | 7 avril 1944 |
| Déclassés | 1972 |
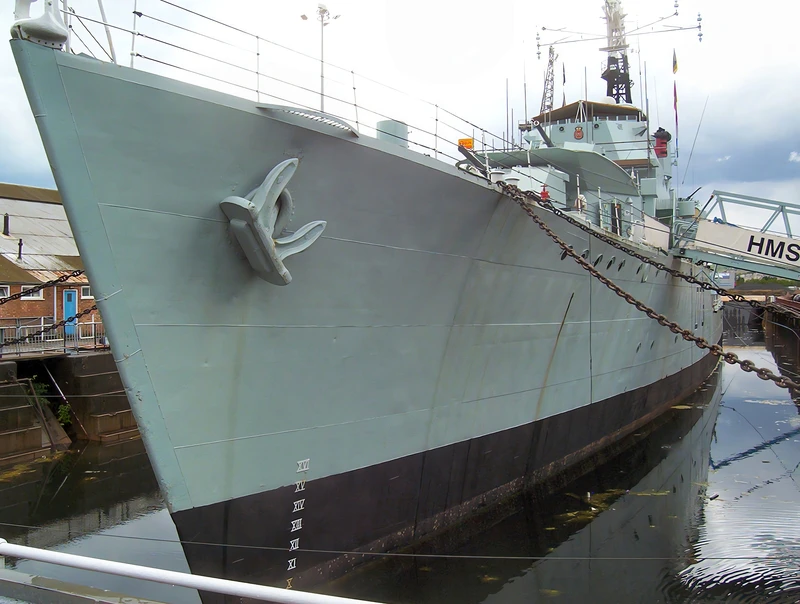
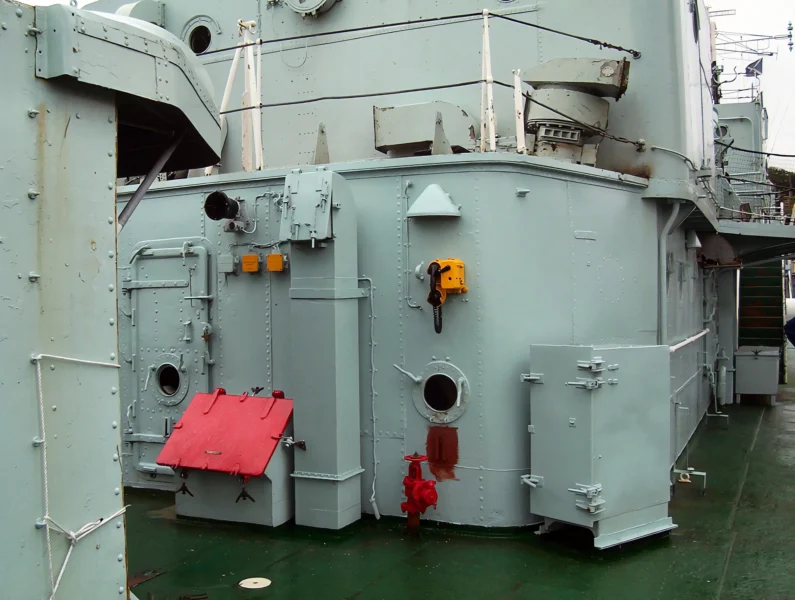
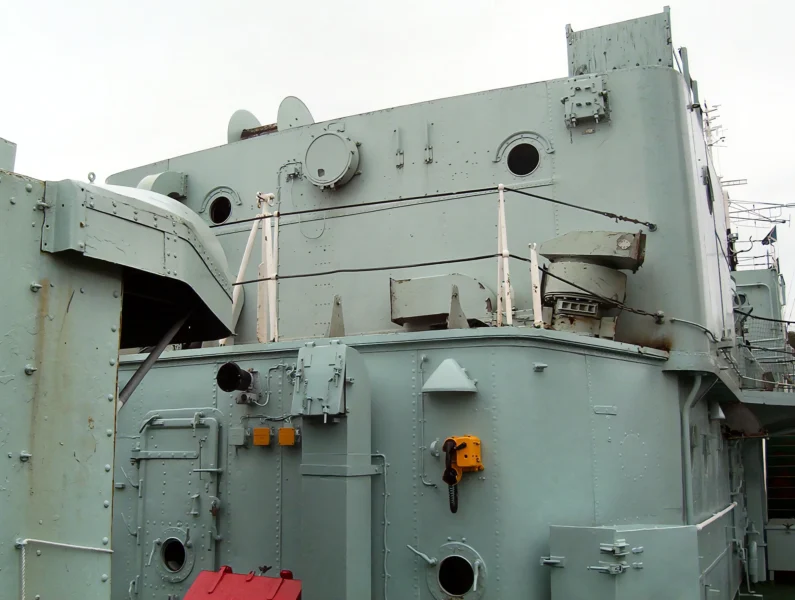
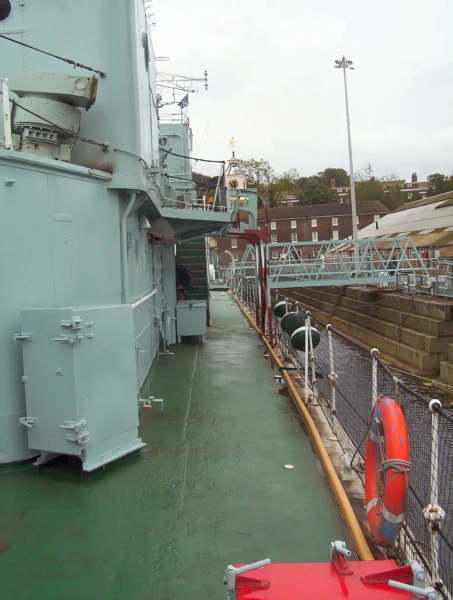
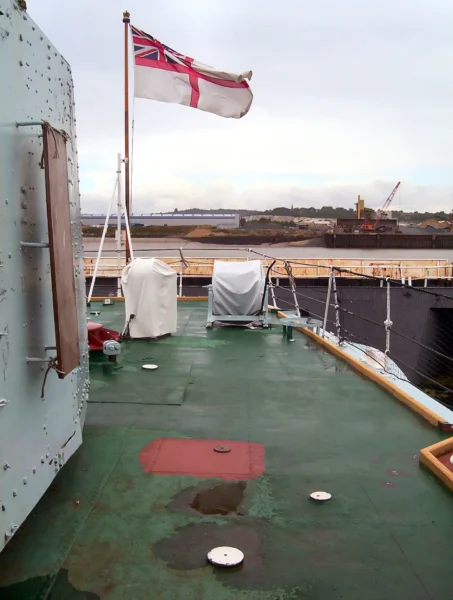
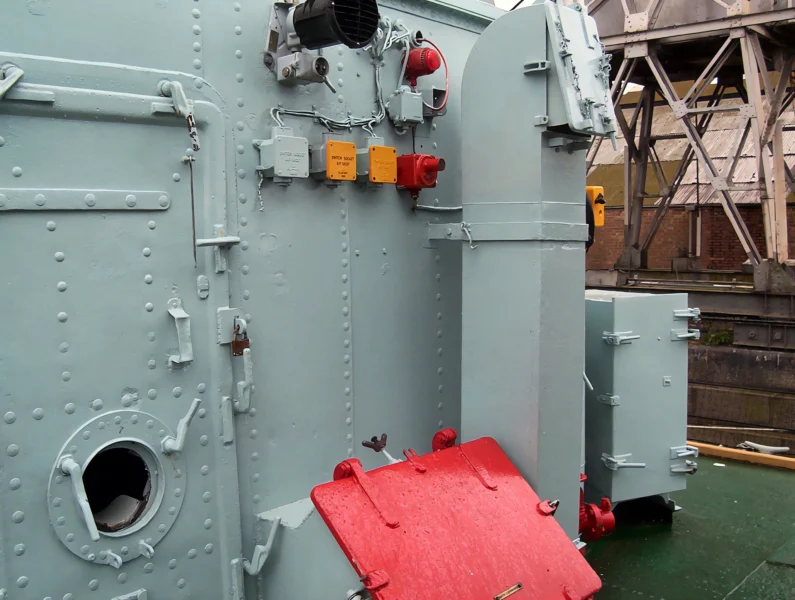
HMS Cavalier est un destroyer de classe C retiré de la Royal Navy. Il a été posé par J. Samuel White and Company à East Cowes le 28 mars 1943, lancé le 7 avril 1944 et mis en service le 22 novembre 1944. Il a servi pendant la Seconde Guerre mondiale et dans diverses commissions en Extrême-Orient jusqu’à ce qu’il soit désarmé en 1972. Après sa mise hors service, il a été préservé en tant que navire musée et réside actuellement au chantier naval historique de Chatham.
Source: HMS Cavalier sur Wikipedia
| HMS Cavalier Walk Around | |
|---|---|
| Photographer | Jon Davies |
| Localisation | Unknow |
| Photos | 174 |
Voir aussi :
General Characteristics and Role
The HMS Cavalier (R73 / D73) was a C-class (Ca-class) destroyer of the Royal Navy (RN) and is the last remaining British World War II-era destroyer, preserved as a museum ship. It was designed for fleet escort and anti-submarine warfare (ASW). Her class was an adaptation of the pre-war J-class destroyer hull, benefiting from partial welding which contributed to its impressive speed. The ship is famous for winning the 1971 « Cock o’ the Fleet » race against the frigate HMS Rapid, proving her exceptional machinery performance even late in her service life.
| Property | Typical Value (HMS Cavalier) |
|---|---|
| Rôle | Fleet Destroyer, Anti-Submarine Escort |
| National Origin | Royaume-Uni |
| Fabricant | J. Samuel White and Company, Cowes |
| commissionné | 22 November 1944 |
| Déclassés | 1972 |
| Displacement (Standard) | 1,710 tons |
| Displacement (Full Load) | 2,520 tons |
| Length (Overall) | 110.5 m (363 ft) |
| Beam | 10.9 m (35 ft 9 in) |
| Crew | Approx. 186 |
| Statut | Preserved museum ship (Chatham Dockyard) |
Propulsion and Performance
- Propulsion: 2 x Parsons geared steam turbines, powered by 2 x Admiralty 3-drum boilers.
- Power Output: 40,000 shaft horsepower (shp).
- Shafts: 2
- Maximum Speed (Design): 37 knots (69 km/h).
- Operational Range: Approximately 1,400 nautical miles at 32 knots (59 km/h).
Armament and Modernization
Initial (WWII) Armament:
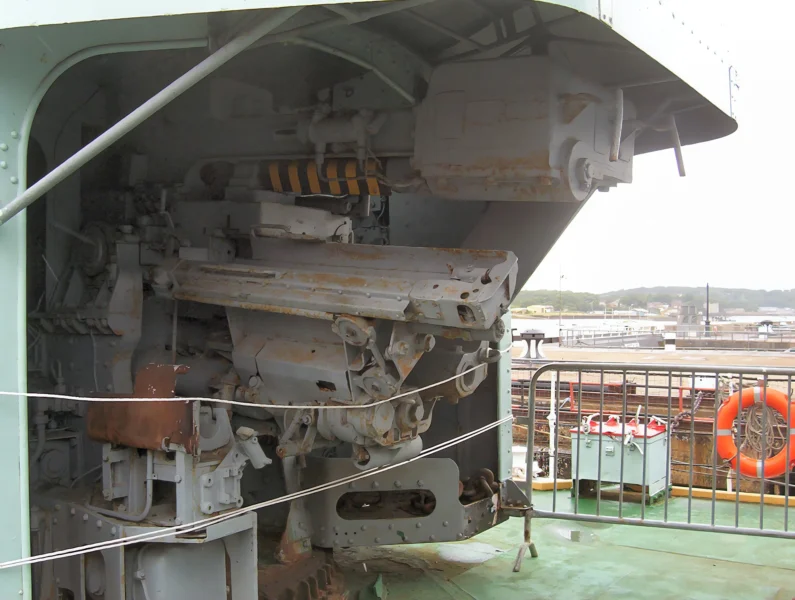
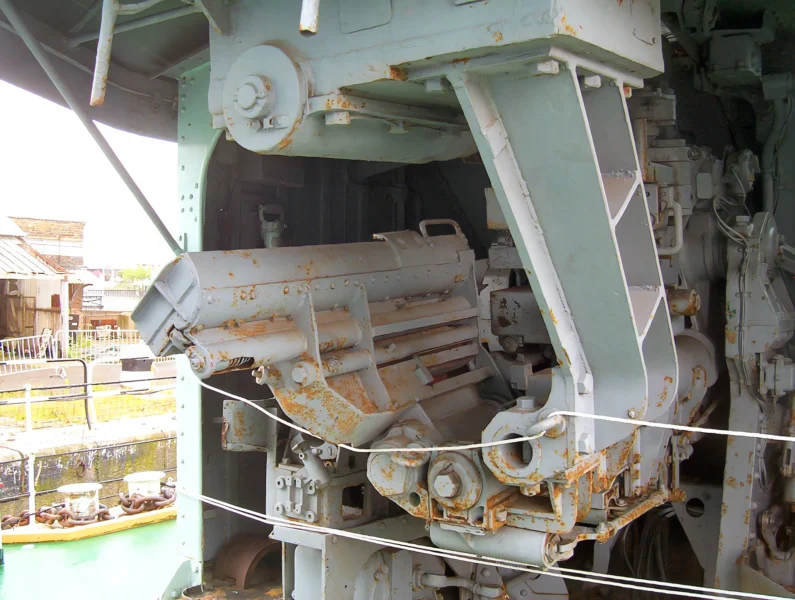
- Main Guns: 4 x QF 4.5-inch (113 mm) Mark IV guns in single mounts.
- Anti-Aircraft (AA): Various light AA guns (e.g., Bofors 40 mm, Oerlikon 20 mm).
- Torpedoes: 8 x 21-inch (533 mm) torpedo tubes in 2 quad mounts.
- Anti-Submarine Warfare (ASW): Depth charge rails and throwers.
Post-War (1950s) Modernization:
- ASW Enhancement: During her 1955-1957 refit, the Squid anti-submarine mortar system (twin three-barrelled mortars that launched depth charges ahead of the ship) was installed.
- Air Defense: Later, in the 1960s, a Seacat surface-to-air missile launcher was added to replace some of her light AA guns.
Vues : 1327