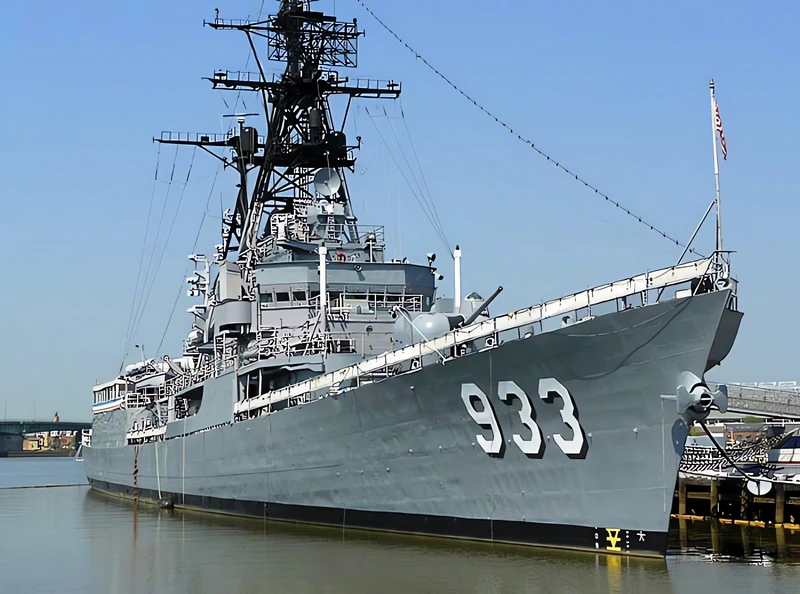
USS Barry (DD-933) | |
|---|---|
| Country | USA |
| Class – Type | Forrest Sherman – class destroyer |
| Launched | 1 October 1955 |
| Decommissioned | 5 November 1982 |
USS Barry (DD-933) was one of eighteen Forrest Sherman–class destroyers of the United States Navy, and was the third US destroyer to be named for Commodore John Barry. Commissioned in 1954, she spent most of her career in the Caribbean, Atlantic, and Mediterranean, but also served in the Vietnam War, for which she earned two battle stars. Another notable aspect of her service was the Cuban Missile Crisis in 1962. Decommissioned in 1982, she became the “Display Ship Barry” (DS Barry), a museum ship at the Washington Navy Yard in Washington, D.C., in 1984.
Source: USS Barry (DD-933) on Wikipedia
| USS Barry Destroyer DD-933 Walk Around | |
|---|---|
| Photographer | Bill Maloney |
| Localisation | Unknow |
| Photos | 227 |
See also:
General Characteristics and Role
The USS Barry (DDG-52) is an Arleigh Burke-class Flight I Aegis guided missile destroyer, currently in active service with the US Navy. She is named in honor of Commodore John Barry, the “Father of the American Navy.” As an Aegis destroyer, her primary role is to serve as a multi-mission surface combatant capable of Anti-Air Warfare (AAW), Anti-Submarine Warfare (ASW), and Anti-Surface Warfare (ASuW). The ship is built around the advanced Aegis Combat System, featuring the powerful AN/SPY-1D multi-function phased array radar, which allows her to track hundreds of targets simultaneously and provide comprehensive fleet defense.
| Property | Typical Value (DDG-52 Flight I) |
|---|---|
| Class & Type | Arleigh Burke-class Guided-Missile Destroyer |
| National Origin | United States |
| Commissioned | 12 December 1992 |
| Propulsion | 4 x General Electric LM2500-30 gas turbines |
| Total Power Output | 100,000 shp (75,000 kW) |
| Length | 154 m (505 ft) |
| Beam | 18 m (59 ft) |
| Displacement (Full Load) | Approx. 8,900 long tons (9,000 t) |
| Speed | In excess of 30 knots (56 km/h) |
Armament and Combat Systems
- Vertical Launch System (VLS): 1 x 29-cell and 1 x 61-cell Mk 41 VLS (90 cells total) for launching Tomahawk cruise missiles, Standard (SM-2/SM-3) surface-to-air missiles, and Vertical Launch Anti-Submarine Rocket (VL-ASROC).
- Gun Armament: 1 x Mk 45 5-inch (127 mm)/54 caliber lightweight gun.
- Close-In Defense: 2 x 20 mm Phalanx Close-In Weapon Systems (CIWS).
- Anti-Submarine Warfare (ASW): Mk 46 torpedoes launched from 2 x triple 12.75 inch Mk 32 torpedo tubes.
- Helicopter Facility: Features a landing deck (Flight I), though full hangar facilities are typically only added in later flights (Flight IIA).
Design Context and Legacy
- Design Philosophy: The Arleigh Burke class introduced a number of major innovations, including the first all-steel combatant hull since World War II (for enhanced durability) and the integrated Aegis system.
- Service History: DDG-52 has received multiple awards for efficiency and combat readiness, including the Battenberg Cup and multiple Battle E awards.
- Modernization: As a Flight I ship, the Barry has undergone significant upgrades, ensuring its combat systems remain relevant, including modernization with Aegis Baseline 9, giving it Ballistic Missile Defense (BMD) capabilities.
Views : 1954