Pansarbandvagn 301 | |
|---|---|
| Land | Schweden |
| Typ | Gepanzerter Personalträger |
| Foto | Thord Wedman |
| Thema | Album von 38 Fotos von einem Panzer Pansarbandvagn 301 |
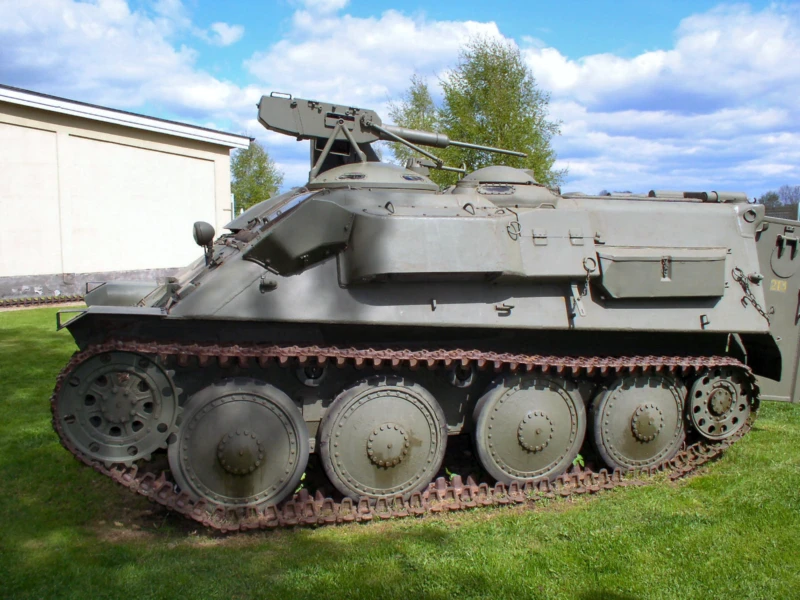
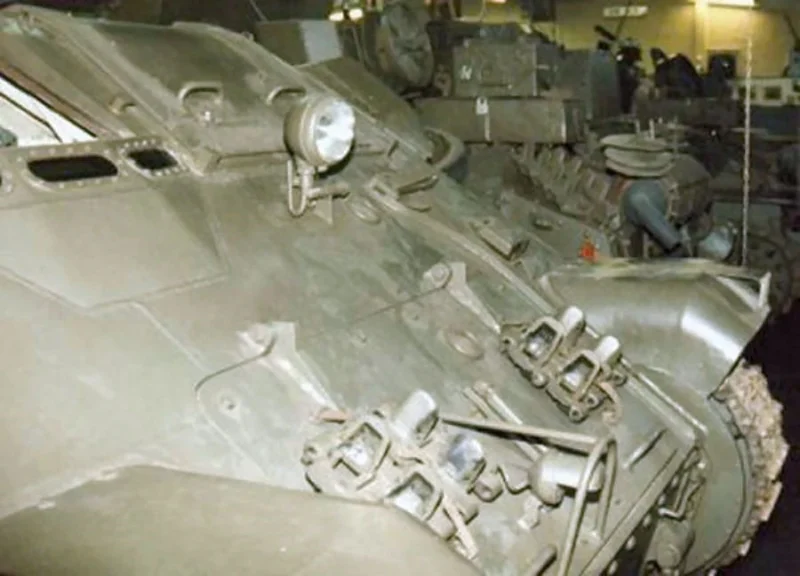
Pansarbandvagn 301 (pbv 301), was a Swedish armoured personnel carrier used by the Swedish Army. It was a typical “battle taxi”, armed with a 20 mm Bofors gun from the scrapped J21-fighters and with room for transporting 8 fully armed soldiers. The pbv 301 was an interim solution, built on the chassis from the obsolete Stridsvagn m/41, introduced in 1961 and removed from service in the late 1960s and early 1970s when the replacement pbv 302 came into use. The pbv 301 replaced the open-topped KP-bil armoured car as the armoured troop transport in the Swedish Army.
Quelle: Pansarbandvagn 301 auf Wikipedia
Siehe auch:
A Masterclass in Military Recycling
das Pansarbandvagn 301 is a fascinating example of Swedish pragmatism. In the late 1950s, the Swedish Army desperately needed an armored personnel carrier (APC) to keep up with their tanks, but the budget was tight. Instead of building from scratch, they took the chassis of the obsolete Stridsvagn m/41 (a licensed copy of the Czech LT vz. 38) and rebuilt them into modern APCs. It served as a vital “stop-gap” vehicle, bridging the era between WWII tankettes and the purpose-built infantry fighting vehicles of the Cold War.
| Attribute | Technical Specification (Pbv 301) |
|---|---|
| Rolle | Armored Personnel Carrier (APC) |
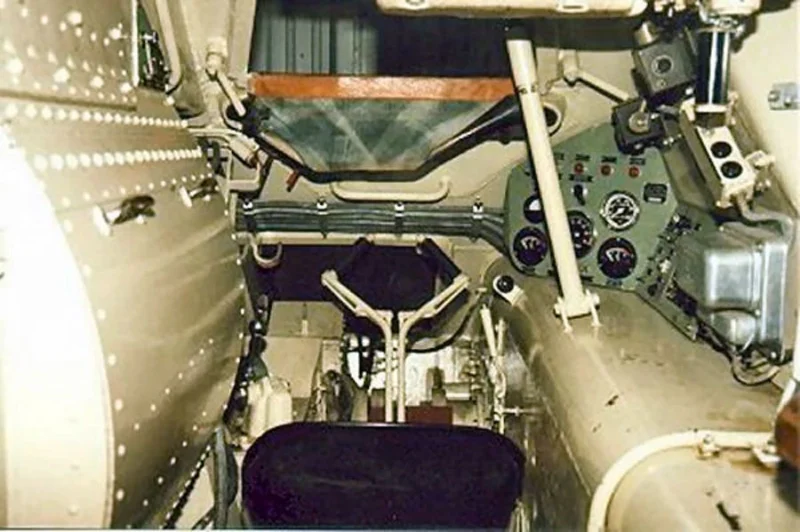
| Crew | 2 (Driver and Gunner) + 7–8 Infantry |
| Fahrgestell | Modified Stridsvagn m/41 (LT vz. 38) |
| Triebwerk | 1 × Svenska Flygmotor B44 (derived from an aircraft engine) |
| Horsepower | 150 hp |
| Höchstgeschwindigkeit | 45 km/h (28 mph) |
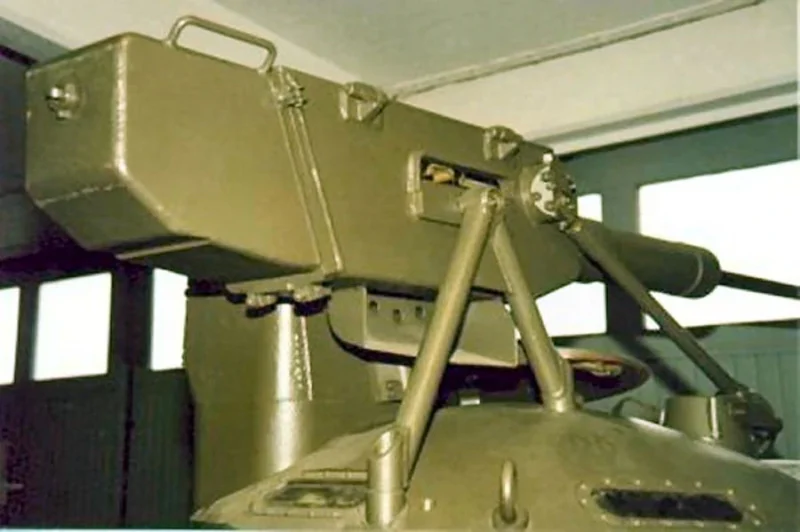
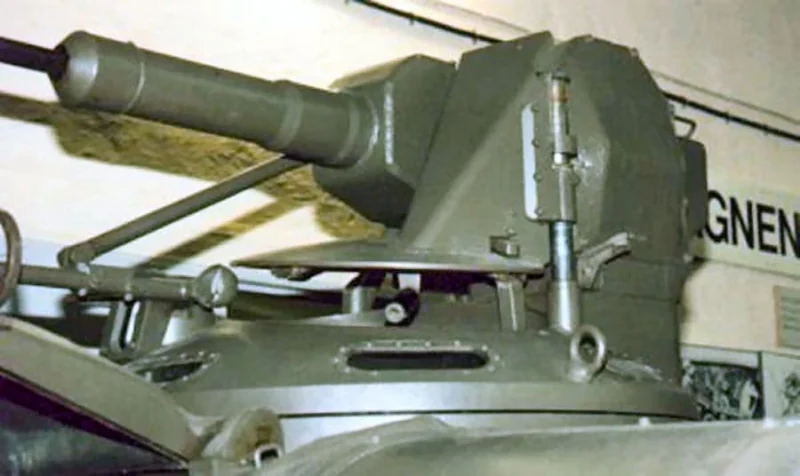
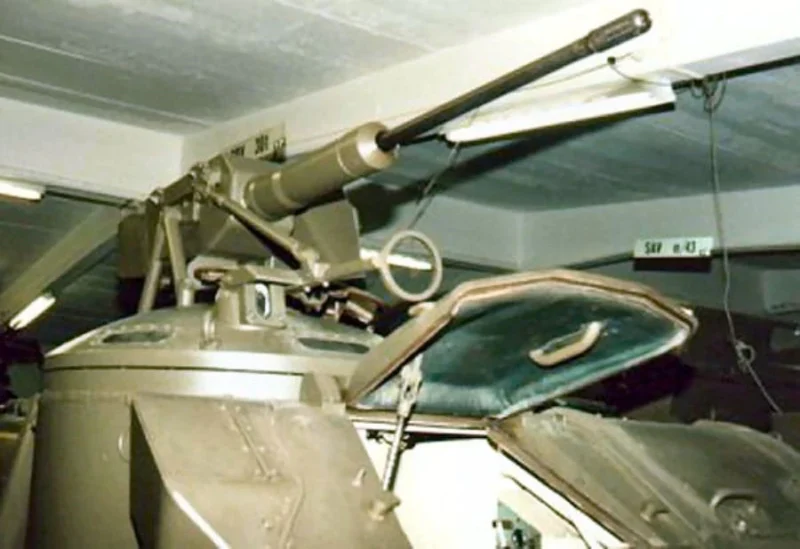
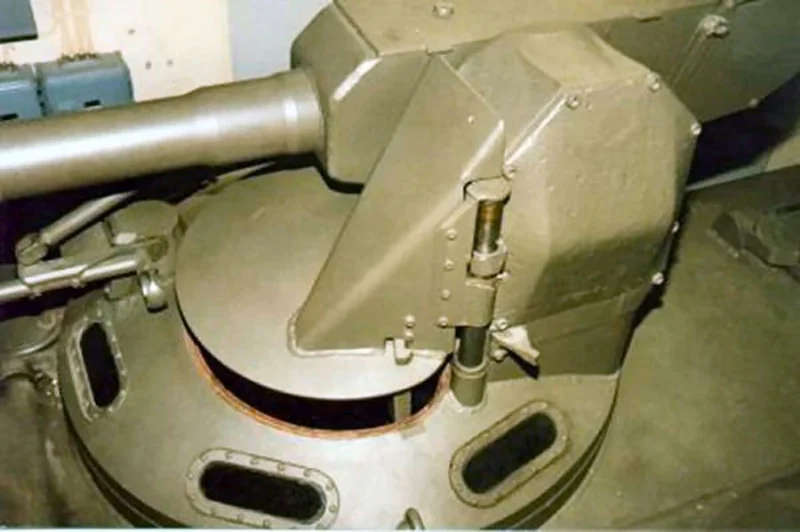
| Hauptbewaffnung | 1 × 20mm m/45B Bofors automatic cannon |
| Amphibious? | Yes (after minimal preparation) |
Design Engineering: Old Bones, New Teeth
- The “Sky” Engine: Because the original tank engine was too large for the APC configuration, Sweden used the Svenska Flygmotor B44, a boxer-style 4-cylinder engine originally intended for light aircraft. It was mounted in the front to leave room for the troop compartment at the rear.
- Recycled Firepower: The 20mm Bofors cannons mounted on the Pbv 301 were not new; they were salvaged from scrapped Saab 21 fighter planes. This “upcycling” gave the infantry significant firepower against light armor and low-flying aircraft.
- The Troop Compartment: Despite its small size, the Pbv 301 featured a rear door and two large roof hatches. This allowed infantry to fire their personal weapons from within the vehicle, essentially making it a precursor to the modern Infantry Fighting Vehicle (IFV).
- Amphibious “Boots”: To cross Sweden’s many lakes, the Pbv 301 was designed to be amphibious. It used its tracks for propulsion in the water, reaching a slow but steady 7 km/h.
Service History: A Bridge to the Future
- Short but Vital Career: The Pbv 301 entered service in 1961 and was retired by 1971. In just one decade, it completely transformed Swedish infantry doctrine from “truck-borne” to “mechanized.”
- The Jungle Variant: While intended for the Swedish forests, the Pbv 301’s design influenced the development of specialized cold-weather vehicles that could navigate the deep snow and marshes of the sub-arctic.
- The Successor: The Pbv 301 was replaced by the Pbv 302, which used a similar layout but was built from the ground up to be a superior combat vehicle with better armor and a more powerful engine.
- Preservation: Several Pbv 301s survive in Swedish museums today (such as Arsenalen), often displayed next to the Strv m/41 to show the incredible transformation from 1940s tank to 1960s APC.
Ansichten : 3133