HMS Cavalier (R73) | |
|---|---|
| Country | United Kingdom |
| Class and type | C-class destroyer |
| Launched | 7 April 1944 |
| Decommissioned | 1972 |
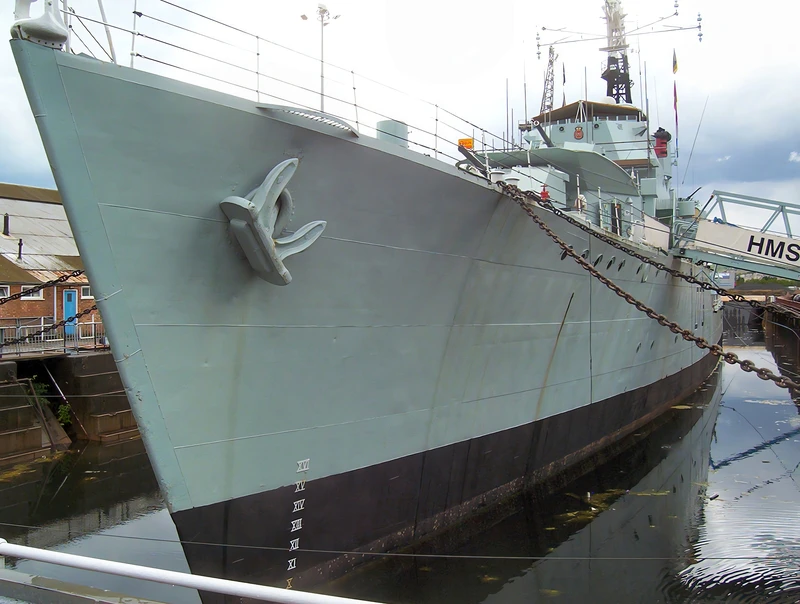
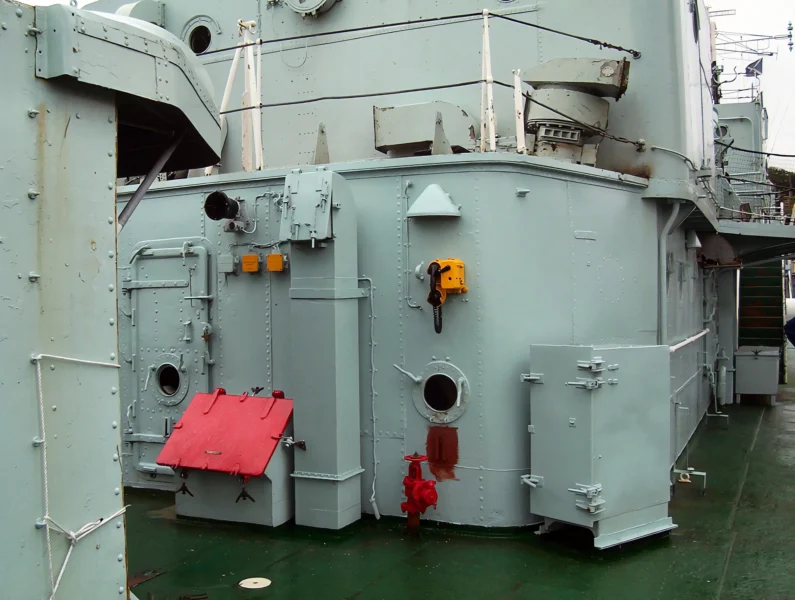
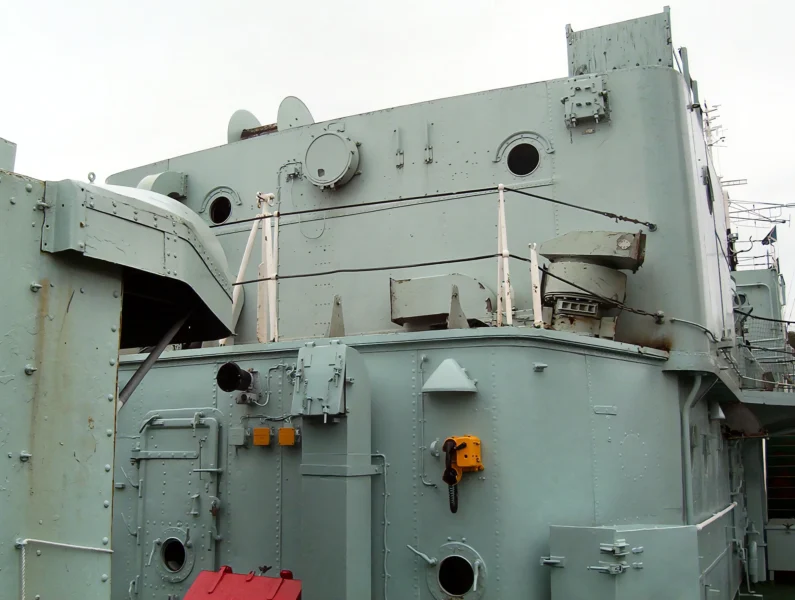
HMS Cavalier is a retired C-class destroyer of the Royal Navy. She was laid down by J. Samuel White and Company at East Cowes on 28 March 1943, launched on 7 April 1944, and commissioned on 22 November 1944. She served in World War II and in various commissions in the Far East until she was decommissioned in 1972. After decommissioning she was preserved as a museum ship and currently resides at Chatham Historic Dockyard.
Source: HMS Cavalier on Wikipedia
| HMS Cavalier Walk Around | |
|---|---|
| Photographer | Jon Davies |
| Localisation | Unknow |
| Photos | 174 |
See also:
General Characteristics and Role
The HMS Cavalier (R73 / D73) was a C-class (Ca-class) destroyer of the Royal Navy (RN) and is the last remaining British World War II-era destroyer, preserved as a museum ship. It was designed for fleet escort and anti-submarine warfare (ASW). Her class was an adaptation of the pre-war J-class destroyer hull, benefiting from partial welding which contributed to its impressive speed. The ship is famous for winning the 1971 “Cock o’ the Fleet” race against the frigate HMS Rapid, proving her exceptional machinery performance even late in her service life.
| Property | Typical Value (HMS Cavalier) |
|---|---|
| Role | Fleet Destroyer, Anti-Submarine Escort |
| National Origin | United Kingdom |
| Manufacturer | J. Samuel White and Company, Cowes |
| Commissioned | 22 November 1944 |
| Decommissioned | 1972 |
| Displacement (Standard) | 1,710 tons |
| Displacement (Full Load) | 2,520 tons |
| Length (Overall) | 110.5 m (363 ft) |
| Beam | 10.9 m (35 ft 9 in) |
| Crew | Approx. 186 |
| Status | Preserved museum ship (Chatham Dockyard) |
Propulsion and Performance
- Propulsion: 2 x Parsons geared steam turbines, powered by 2 x Admiralty 3-drum boilers.
- Power Output: 40,000 shaft horsepower (shp).
- Shafts: 2
- Maximum Speed (Design): 37 knots (69 km/h).
- Operational Range: Approximately 1,400 nautical miles at 32 knots (59 km/h).
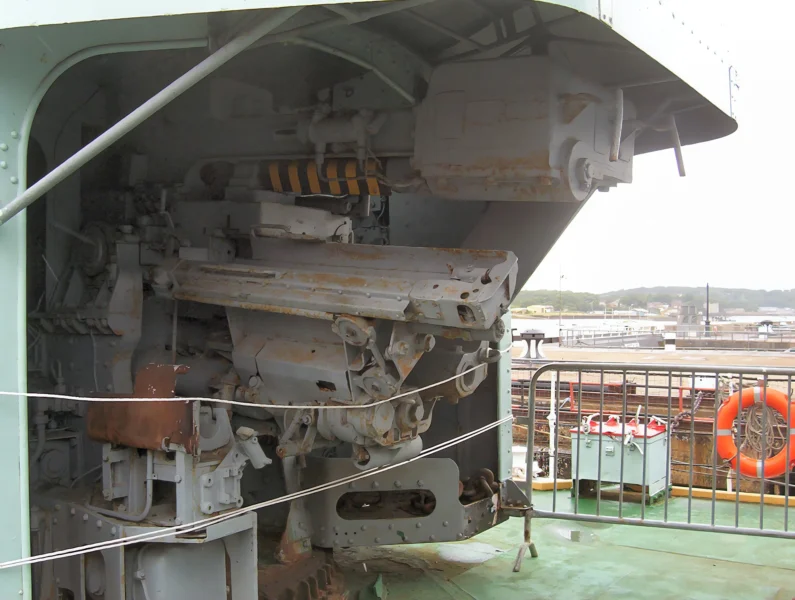
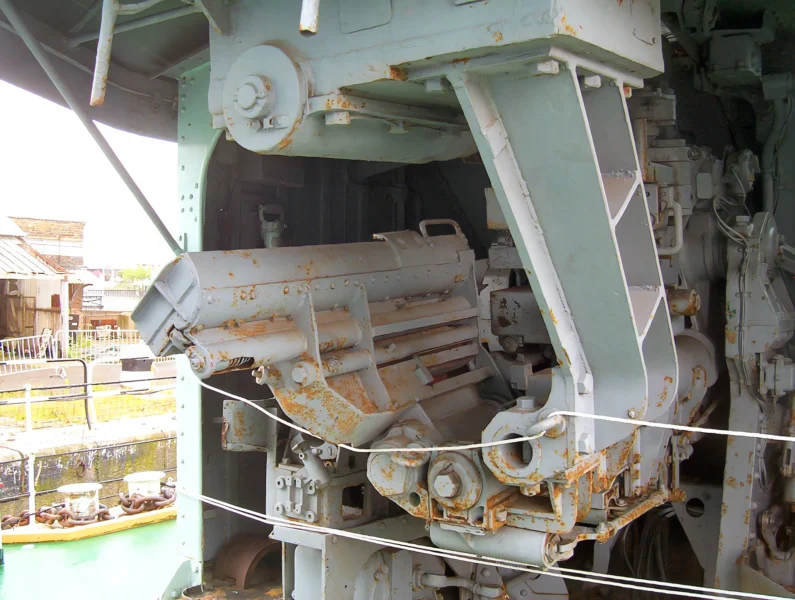
Armament and Modernization
Initial (WWII) Armament:
- Main Guns: 4 x QF 4.5-inch (113 mm) Mark IV guns in single mounts.
- Anti-Aircraft (AA): Various light AA guns (e.g., Bofors 40 mm, Oerlikon 20 mm).
- Torpedoes: 8 x 21-inch (533 mm) torpedo tubes in 2 quad mounts.
- Anti-Submarine Warfare (ASW): Depth charge rails and throwers.
Post-War (1950s) Modernization:
- ASW Enhancement: During her 1955-1957 refit, the Squid anti-submarine mortar system (twin three-barrelled mortars that launched depth charges ahead of the ship) was installed.
- Air Defense: Later, in the 1960s, a Seacat surface-to-air missile launcher was added to replace some of her light AA guns.
Views : 1326