M7B2 Священик | |
|---|---|
| Платить | Сша |
| Тип | Самохідна гармата |
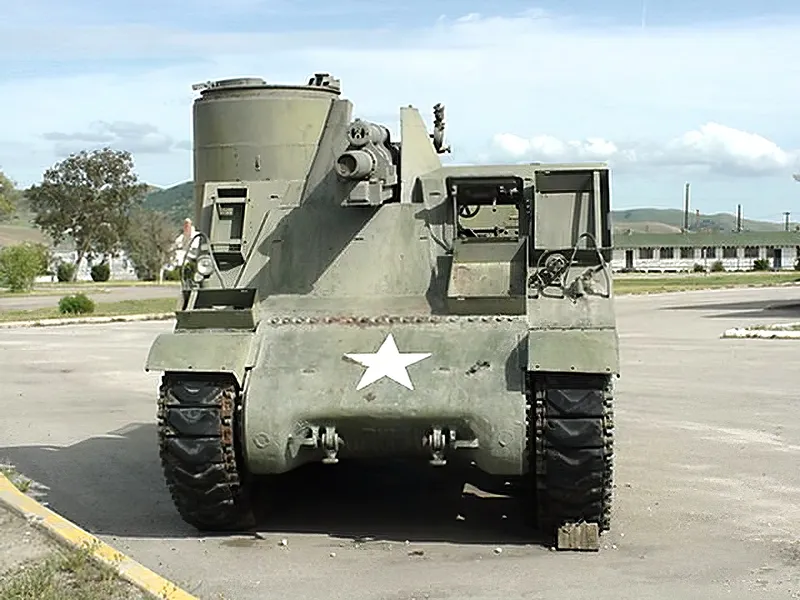
Офіційно позначений як 105-мм гаубичний мотоколяска M7, M7 Священик — самохідна артилерійська установа, що випускалася під час Другої світової війни США. Жрець est le surnom donné par les Britanniques, dû au fait que la mitrailleuse placée sur un rail donnait l’impression que le char était muni d’une chaire. Il faisait suite au Bishop anglais et ils le désignèrent officiellement 105mm SP Priest.
Джерело: M7 Priest у Вікіпедії
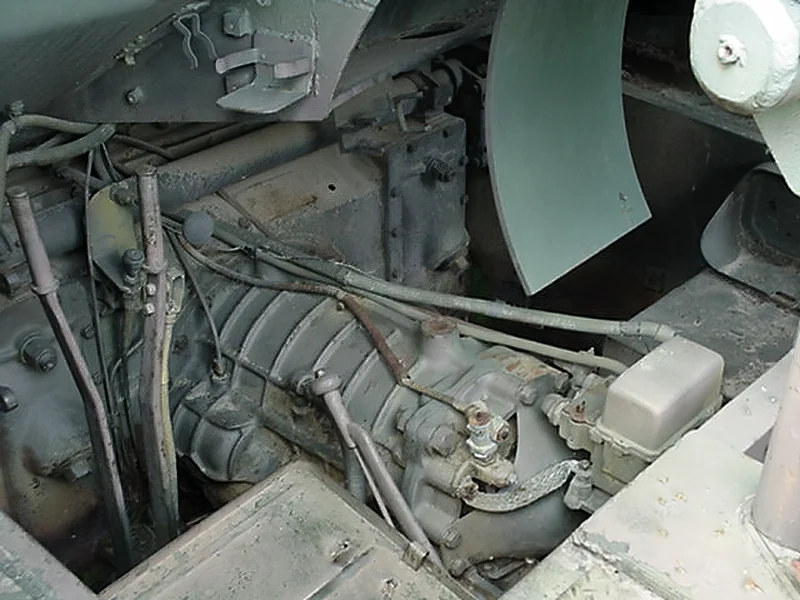
Технічні характеристики: Équipage : 7 Longueur : 6,02 m Largeur : 2,87 m Hauteur : 2,95 m Masse au combat : 22 970 kg Blindage : coque:51 mm avant Armement principal : Howitzer 105 mm M2A1 (69 obus) Armement secondaire : 1 Mitrailleuse Browning M2 de 12,7 mm (300 balles) Moteur : Wright (Continental) R975 C1 400 ch (299 kW) Suspension : ressorts verticaux en spirales Vitesse sur route : 40 km/h (24 en tout terrain) Puissance massique : 17,4 ch/tonne Autonomie : 193 km
| M7B2 Walk Around | |
|---|---|
| Фотограф | Unknow |
| Локалізацією | Незнай |
| Фото | 25 |
Читайте також:
Development and Design
The M7 was developed in 1941 to provide the US Army with a fully tracked, armored vehicle capable of delivering indirect fire. This was necessary because existing towed artillery could not keep up with the speed of armored advances.
- Chassis: The vehicle was initially built on a modified M3 Lee medium tank chassis. Later versions, like the M7B1, transitioned to the more advanced M4 Sherman chassis.
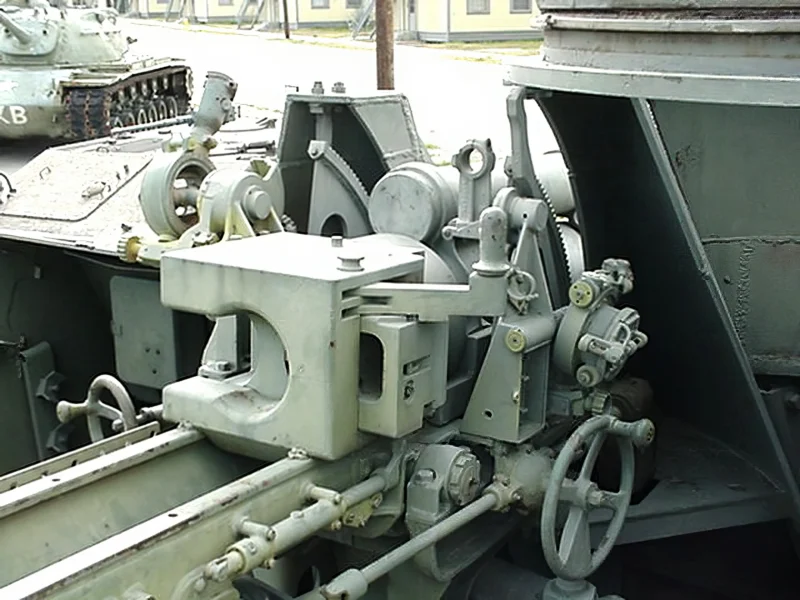
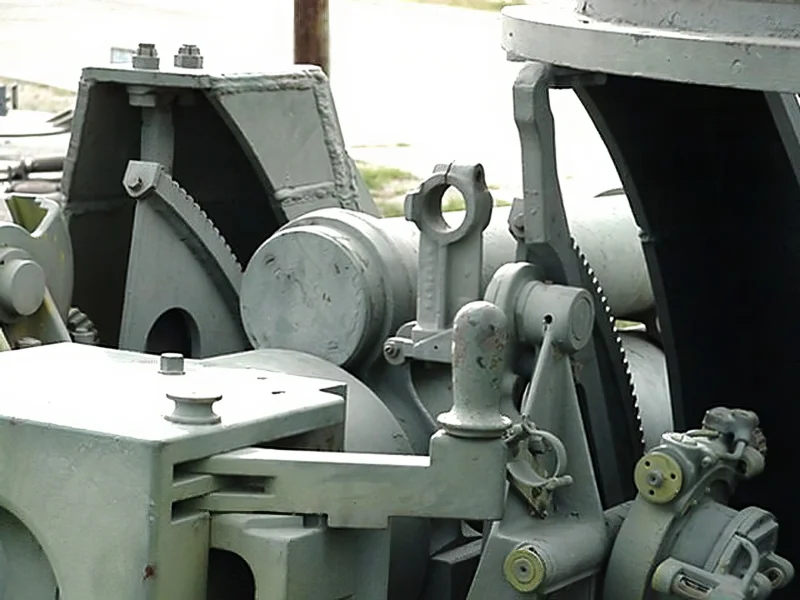
- Armament: The main weapon was the powerful 105 mm M2 Howitzer, mounted in an open-topped superstructure. This allowed the gun crew to operate with high elevation for indirect fire.
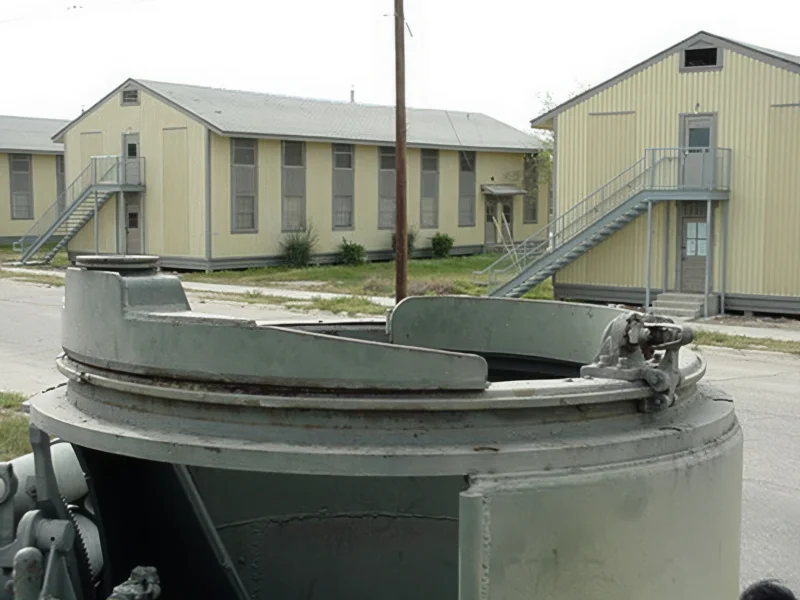
- Secondary Weapon: A unique feature was the “pulpit-like” mount for a .50 caliber M2 Browning heavy machine gun, which provided anti-aircraft defense and close-range protection for the crew.
- Mobility: Despite its size, the M7’s tracked chassis gave it excellent off-road mobility, allowing it to move quickly to new firing positions (a tactic known as “shoot-and-scoot”).
Історія експлуатації
The M7 Priest served with US, British, and Commonwealth forces in every major theater of World War II, starting with combat debut in the North African campaign.
- North Africa and Italy: It was first used in the Second Battle of El Alamein by the British Eighth Army, proving its value immediately by providing rapid, effective fire support.
- Western Front: During the Normandy invasion (D-Day) and the subsequent drive across Europe, the M7 was a standard component of US armored divisions. It provided devastating preparatory and supporting fire, often firing high-explosive shells, smoke rounds, and occasionally, anti-tank rounds.
- Pacific Theater: The M7 was also used effectively in the Pacific, where its high-trajectory howitzer could fire over dense jungle to hit Japanese fortifications and provide close support for infantry assaults.
- Post-War Service: The M7 Priest remained in service with many armies worldwide into the 1950s, seeing action again in the Korean War.
Specifications (M7 Priest)
| Characteristic | Specification |
|---|---|
| Official Designation | 105-мм гаубичний моторний лафет M7 |
| Тип | Self-Propelled Howitzer (SPG) |
| Масового | 22.9 metric tons (22.5 long tons) |
| команда | 5–6 (Commander, Driver, Gunner, Loader, etc.) |
| Основне озброєння | 105 mm Howitzer M2A1 |
| Двигун | Continental R975 C1 9-cylinder radial gasoline engine (350–400 hp) |
| Max Speed (Road) | 42 km/h (26 mph) |
| Діапазон | 190 km (120 miles) |
Views : 3232