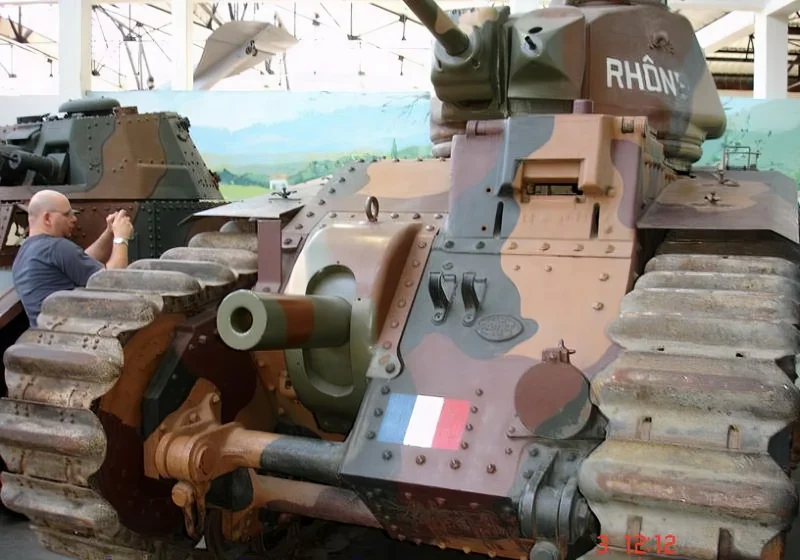
B1 bis | |
|---|---|
| Riik | Prantsusmaa |
| Tüüp | Raske chard |
| Char Renault B1 bis – WalkAround | |
|---|---|
| Fotograaf | Unknow |
| Lokaliseerimine | Teadmata |
| Fotod | 64 |
| Char B1 bis Walk Around | |
|---|---|
| Fotograaf | Unknow |
| Lokaliseerimine | Teadmata |
| Fotod | 26 |
Vaata ka:
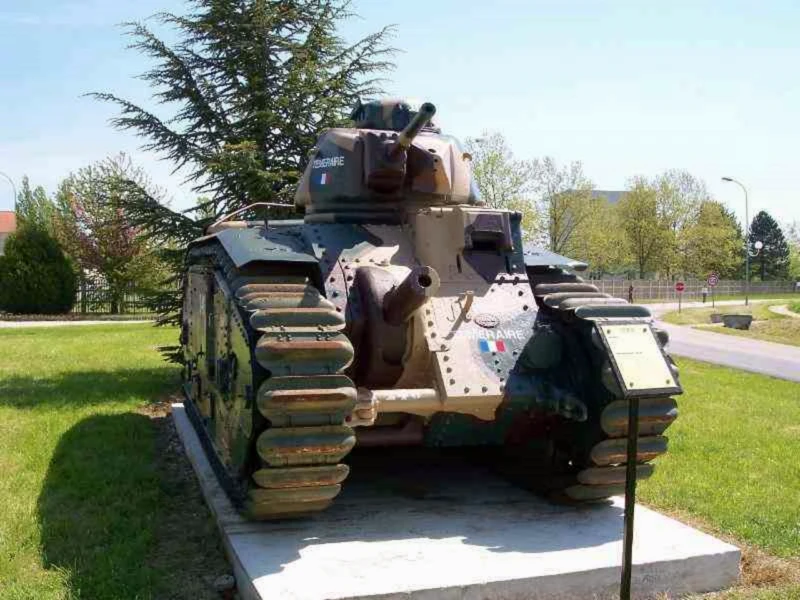
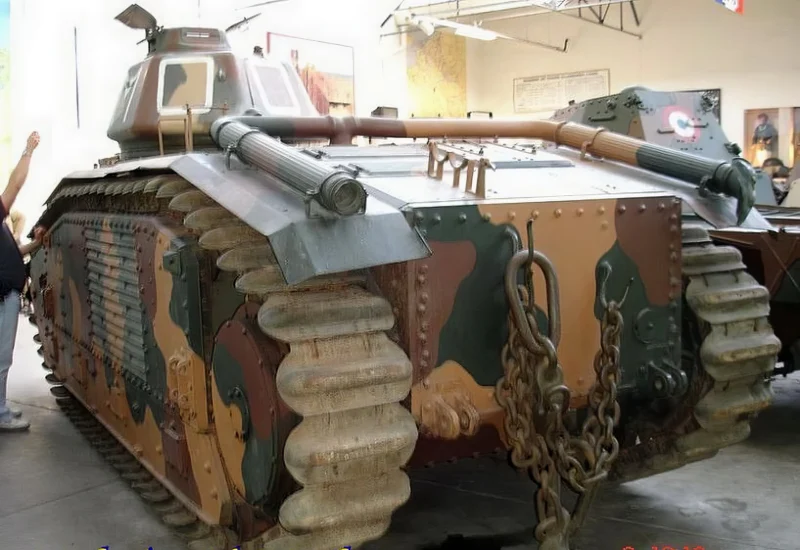
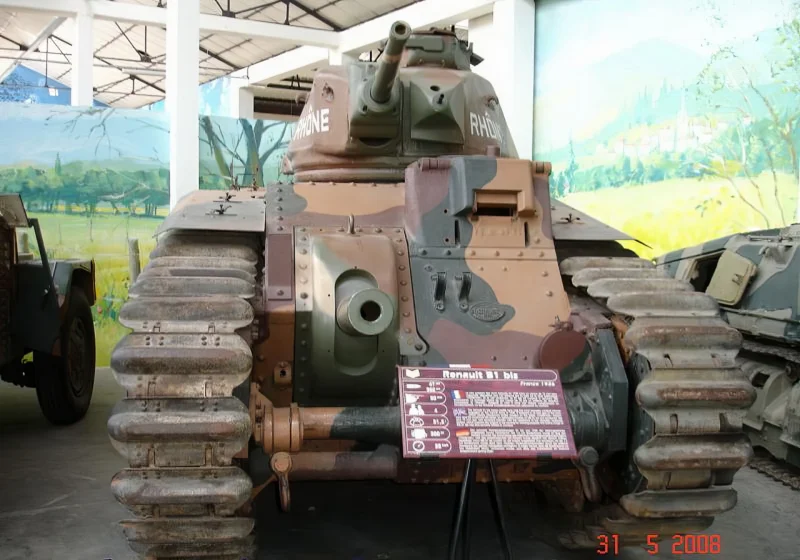
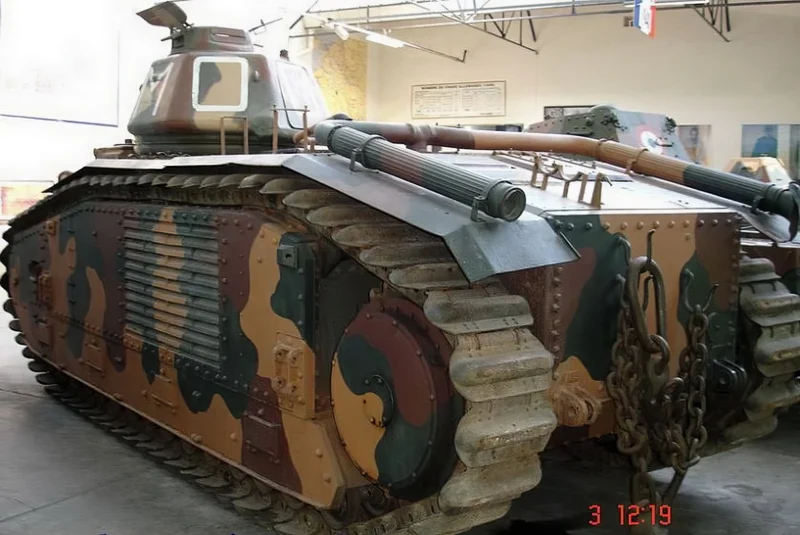
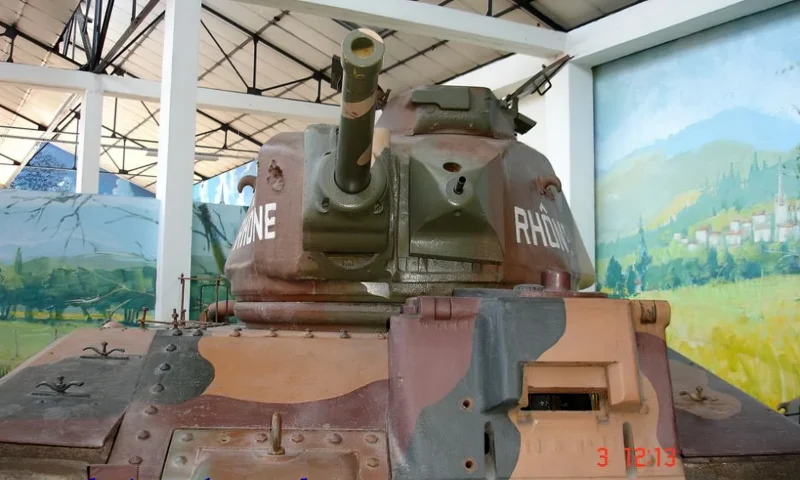
2007 Char B1 bis was a heavy infantry support tank designed and produced by France in the interwar period. It was the principal and most formidable variant of the Char B1 series used during the Battle of France in 1940.
Design Philosophy and Development
Conceived in the 1920s as a “Battle Tank” (Char de Bataille), its original role was a breakthrough vehicle, designed to lead assaults against fortified positions while supporting infantry. This led to a very complex and heavily armored design for its time.
Key Specifications (B1 Bis)
| Characteristic | Väärtus |
|---|---|
| Rolli | Heavy/Breakthrough Tank |
| Mass | Approximately 31.5 tonnes |
| Armor (Maximum) | 60 mm (Frontal hull/turret), 55 mm (Side hull) |
| Mootor | Renault 6-cylinder petrol engine (~300 hp) |
| Max Speed (Road) | ~28 km/h (17 mph) |
| Meeskonna | 4 (Commander/Gunner, Driver/Hull Gunner, Loader, Radio Operator) |
Unique Armament and Flaws
The B1 bis featured a highly unusual and complex dual-gun armament setup:
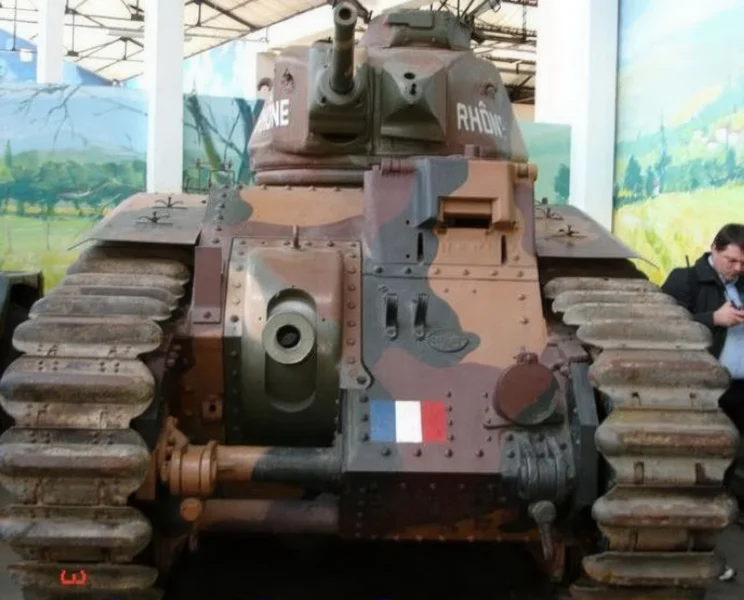
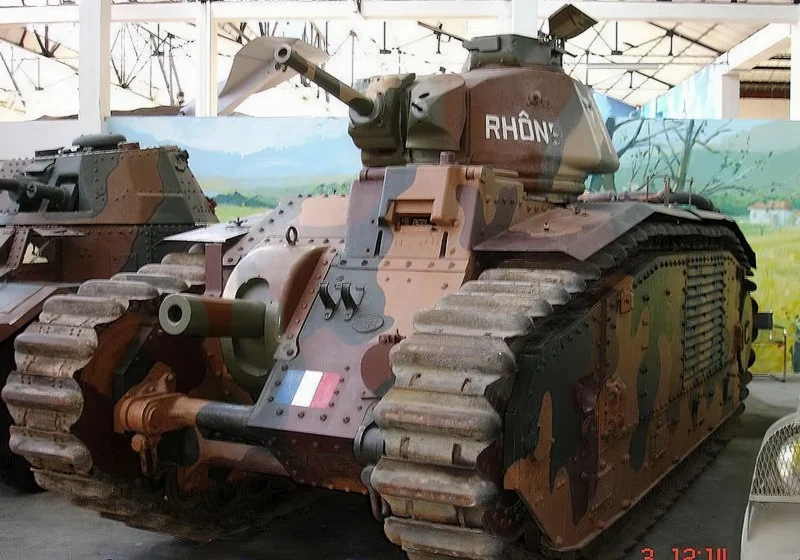
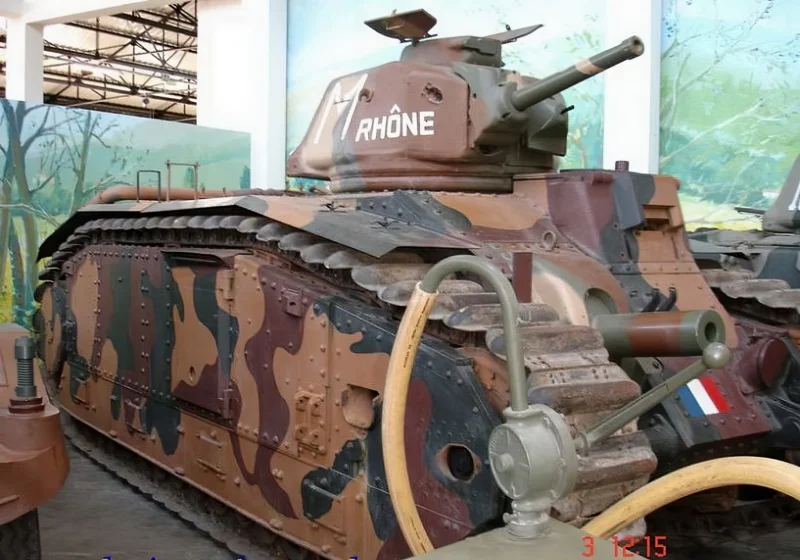
- Hull Gun: A powerful 75 mm SA 35 howitzer fixed in the front right of the hull. To aim this gun horizontally, the driver had to turn the entire tank using a specialized Naeder hydraulic transmission, a significant tactical limitation.
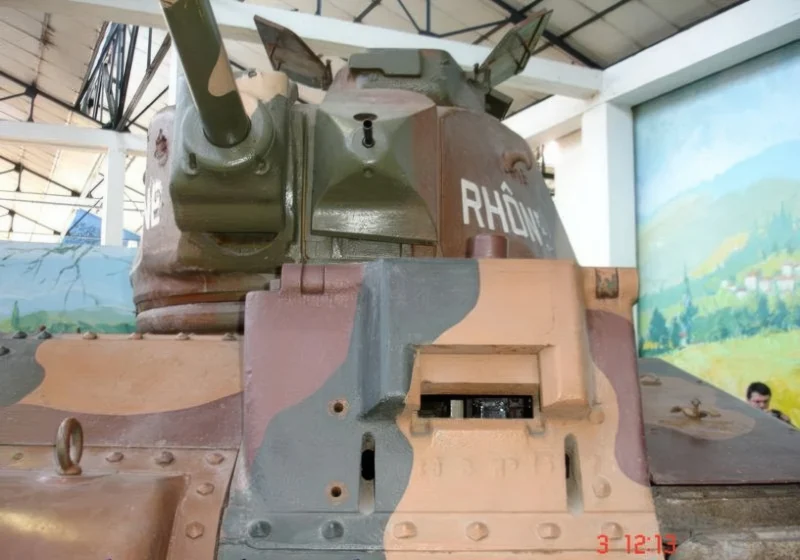
- Turret Gun: A high-velocity 47 mm SA 35 anti-tank gun was mounted in the single-man APX4 turret, alongside a 7.5 mm machine gun.
- Overburdened Commander: The most critical flaw was the single-man turret. The tank commander was responsible for locating targets, aiming, loading, and firing the 47 mm gun, and commanding the tank (and often the platoon), severely limiting combat effectiveness and situational awareness.
Performance in the Battle of France (1940)
- Armored Strength: Its heavy armor (up to 60 mm) made it nearly impervious to most standard German anti-tank guns and tank guns (like the 3.7 cm PaK 36) at typical combat ranges.
- Notable Action: The B1 bis earned a legendary reputation for durability. In one famous engagement at Stonne, a single B1 bis tank, named “Eure,” absorbed over 140 hits from German anti-tank and tank guns without being penetrated, managing to destroy multiple German tanks.
- Strategic Weaknesses: Despite its strength, its very slow speed, complex maintenance, and extremely high fuel consumption (requiring frequent and vulnerable refueling stops) made it poorly suited for the mobile warfare (Blitzkrieg) employed by the German forces.
Aftermath
Following the Fall of France, many captured Char B1 bis tanks were subsequently pressed into service by the German Wehrmacht, primarily designated as Panzerkampfwagen B2 740 (f), and were often used for training, internal security, or converted into self-propelled guns and flamethrower tanks (Flammpanzer B2 (f)).
Vaatamisi: 5180